Trenchless technology, a groundbreaking innovation in the construction industry, offers a myriad of advantages and applications, revolutionizing the way we install and maintain underground infrastructure. Its unique methods minimize environmental impact, reduce project duration, and enhance safety, making it an indispensable tool for modern infrastructure development.
From installing new pipelines to rehabilitating aging ones, trenchless technology has transformed the industry, offering a cost-effective and efficient alternative to traditional excavation methods. This innovative approach is rapidly gaining traction worldwide, with countless successful projects showcasing its versatility and benefits.
Planning and Design Considerations
Trenchless projects require meticulous planning and design to ensure successful execution and minimize potential risks. Several factors must be taken into account to optimize the project outcome.
Geological Considerations:
- Soil type and composition: The nature of the soil, including its density, grain size, and moisture content, influences the choice of trenchless method and the required equipment.
- Presence of obstacles: Subsurface utilities, rock formations, and other obstacles can affect the feasibility and design of the trenchless project.
- Groundwater conditions: High groundwater levels can pose challenges during trenchless operations, requiring additional measures for dewatering and managing water flow.
Environmental Considerations:
- Environmental impact: Trenchless methods aim to minimize surface disruption and environmental impact. However, potential effects on vegetation, wildlife, and water resources must be assessed.
- Noise and vibration: Trenchless operations can generate noise and vibrations that may affect nearby communities or sensitive ecosystems.
- Air quality: Emissions from equipment and materials used in trenchless projects must be considered and managed to comply with environmental regulations.
Infrastructure Considerations:
- Existing infrastructure: The location and depth of existing utilities, roads, and other infrastructure must be carefully identified to avoid conflicts and ensure the safety of the project.
- Traffic management: Trenchless projects may require temporary traffic diversions or closures, which must be planned in advance to minimize disruption.
- Coordination with stakeholders: Effective communication and coordination with utility owners, property owners, and the general public are crucial to ensure smooth project implementation and minimize inconvenience.
Equipment and Materials
Trenchless operations rely on specialized equipment and materials to effectively execute underground construction and repair projects.
Equipment used in trenchless technology includes:
- Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) rigs:These rigs are designed to bore underground by drilling a pilot hole and then enlarging it to accommodate pipes or other utilities.
- Microtunneling machines:These machines are used for smaller-diameter installations and provide precise excavation and pipe placement capabilities.
- Pipe bursting equipment:This equipment involves bursting existing pipes and replacing them with new ones, minimizing disruption to the surrounding area.
- Cured-in-place pipe (CIPP) systems:These systems involve inserting a flexible liner into an existing pipe and curing it in place, creating a new, leak-proof lining.
Materials employed in trenchless operations include:
- Pipes:Trenchless operations utilize various types of pipes, including high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and ductile iron, depending on the specific application and requirements.
- Liners:Liners are used to rehabilitate existing pipes and can be made from materials such as polyethylene, felt, or fiberglass.
Construction and Installation
Trenchless technology involves a range of methods for installing or replacing underground utilities without excavating a trench. These methods are employed to minimize surface disruption, reduce environmental impact, and maintain existing infrastructure.
Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD)
- Involves drilling a pilot hole along the desired path, followed by reaming the hole to a larger diameter.
- The product pipe is then pulled back through the reamed hole.
HDD is suitable for installing pipelines, conduits, and cables under obstacles such as roads, rivers, and railways.
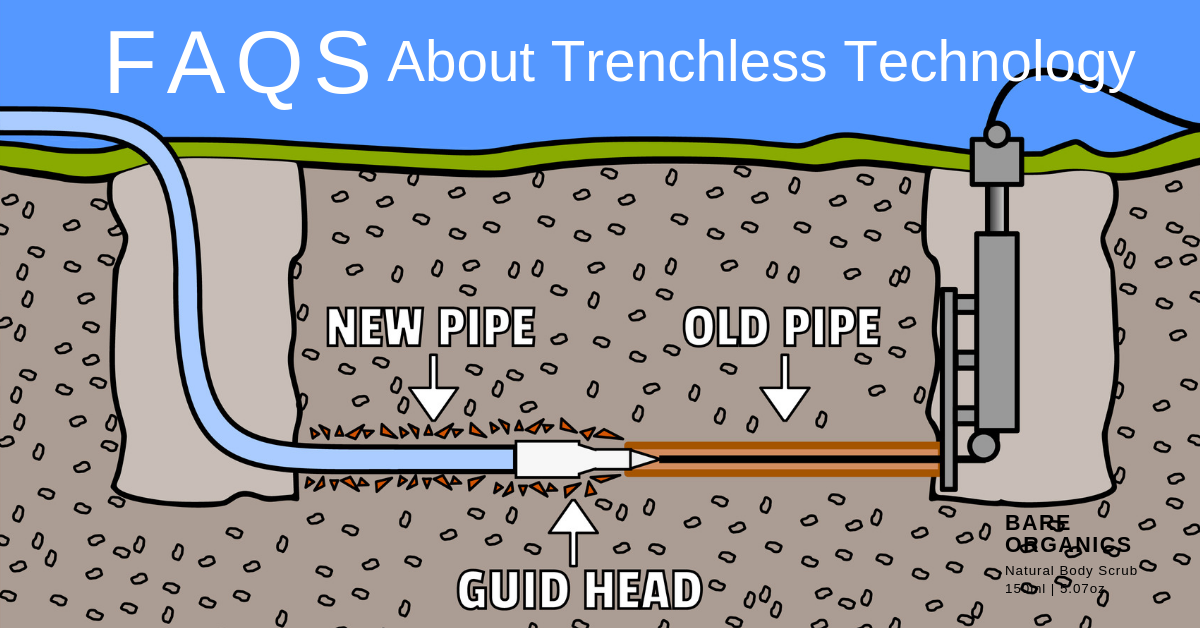
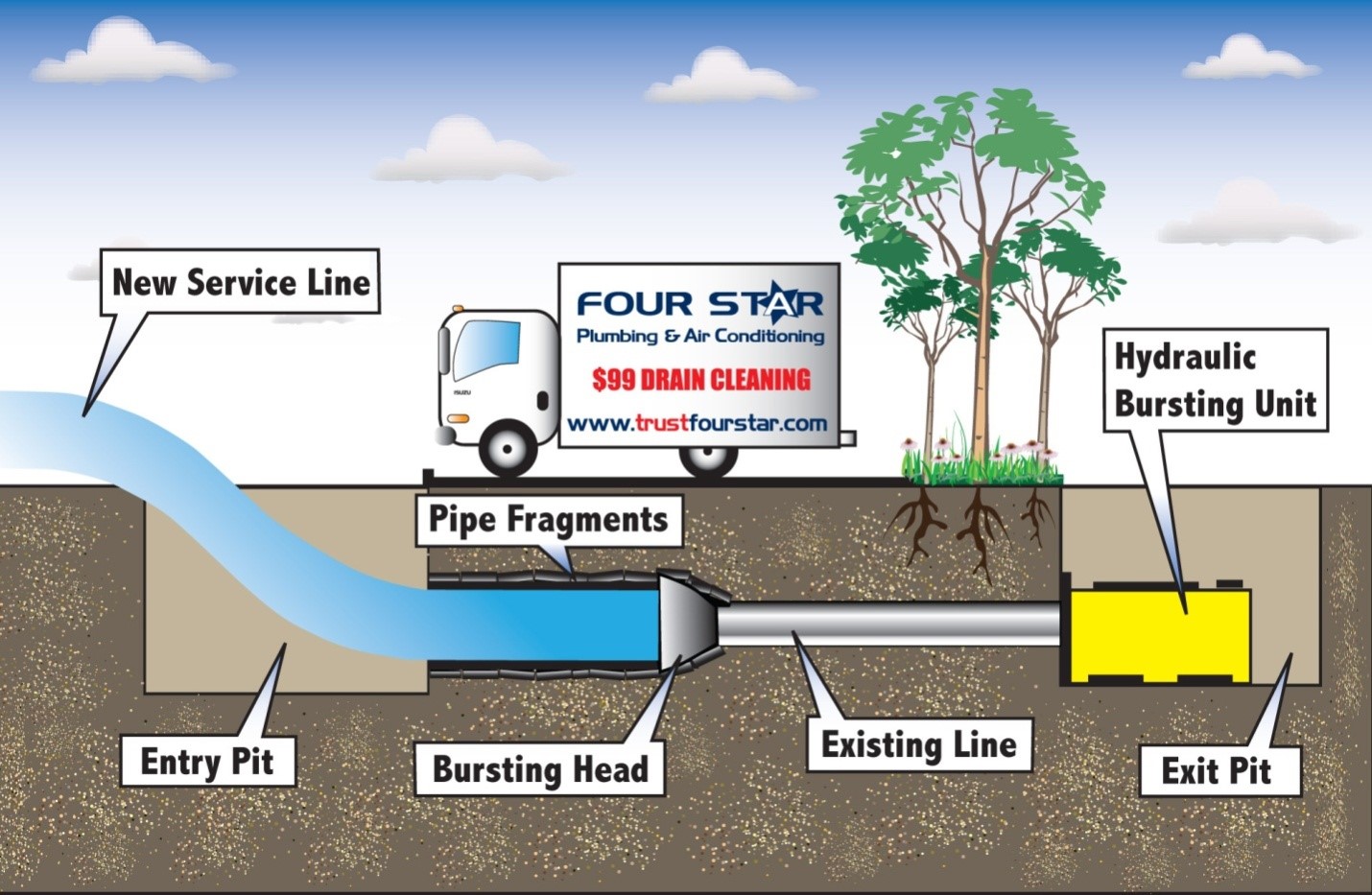
Pipe Bursting
- Employs a bursting head attached to a new pipe to break through an existing pipe.
- The new pipe is simultaneously pulled into place as the old pipe is shattered.
Pipe bursting is used to replace aging or damaged pipes with minimal disruption to the surrounding environment.
Microtunneling
- Involves excavating a small-diameter tunnel using a microtunneling boring machine (MTBM).
- The MTBM simultaneously installs a pipe or casing behind it.
Microtunneling is suitable for constructing tunnels in densely populated areas or where surface disruption is undesirable.
Auger Boring
- Uses an auger to bore a hole along the desired path.
- The product pipe is then pushed or pulled into the hole.
Auger boring is suitable for installing pipelines and conduits in soft ground conditions.
Inspection and Maintenance
Trenchless installations require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure their continued performance and longevity. Several methods and technologies are employed for this purpose, ranging from visual inspections to advanced diagnostic techniques.
Visual inspections involve examining the installation for any visible signs of damage or deterioration, such as cracks, leaks, or misalignments. This can be done through direct observation or using specialized equipment like cameras and endoscopes.
Advanced Inspection Techniques
Advanced inspection techniques provide more detailed and comprehensive assessments of trenchless installations. These include:
- Closed-Circuit Television (CCTV) Inspection:CCTV cameras mounted on robotic crawlers are inserted into the installation to capture high-resolution images and videos, allowing for a thorough visual inspection.
- Acoustic Leak Detection:Sensitive microphones are used to detect leaks by listening for the sound of escaping fluids.
- Radiographic Inspection:X-rays or gamma rays are used to create images of the installation, revealing any internal defects or anomalies.
Maintenance Considerations, Trenchless technology
Regular maintenance is crucial for trenchless installations. This may include:
- Cleaning and Flushing:Periodic cleaning and flushing remove debris and sediment accumulation, maintaining the flow capacity and preventing blockages.
- Rehabilitation:In cases of damage or deterioration, trenchless rehabilitation techniques can be used to repair or restore the installation without the need for excavation.
- Monitoring and Data Collection:Sensors and monitoring systems can be installed to collect data on the performance and condition of the installation, enabling proactive maintenance and early detection of potential issues.
Case Studies and Success Stories

Trenchless technology has been successfully employed in various projects worldwide, delivering significant benefits and overcoming challenges. These case studies showcase the real-world applications and outcomes of trenchless methods.
The successful implementation of trenchless projects requires careful planning, design, and execution. Proper site assessment, material selection, and construction techniques are crucial for achieving desired outcomes. These case studies provide valuable insights into the factors contributing to project success.
Subterranean Sewer Rehabilitation in New York City
- Project Details:Rehabilitation of a 120-year-old sewer line using cured-in-place pipe (CIPP) technology.
- Challenges:Deteriorated sewer line, limited access, and dense urban environment.
- Outcomes:Successful rehabilitation without disrupting traffic or excavating the road, extending the sewer’s lifespan by over 50 years.
Environmental Impact
Trenchless technology is an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional excavation methods, offering significant benefits for the preservation of ecosystems and natural resources.Compared to open-cut excavation, trenchless methods minimize surface disruption, reducing the impact on vegetation, wildlife, and soil erosion. They also eliminate the need for large machinery and heavy vehicles, reducing noise pollution, air emissions, and carbon footprint.
Benefits for Soil and Water
Trenchless techniques preserve soil structure and prevent soil compaction, which is crucial for maintaining soil health and water infiltration. By minimizing excavation and reducing surface disturbance, these methods protect water bodies from sediment runoff and pollution.
Protection of Vegetation and Wildlife
Trenchless technology allows for the installation of underground infrastructure without disturbing vegetation or disrupting wildlife habitats. It preserves trees, shrubs, and other plant life, maintaining the ecological balance and biodiversity of the area.
Future Trends and Innovations
Trenchless technology continues to evolve, with new technologies and innovations emerging to enhance its capabilities and applications. These advancements promise to further improve the efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability of trenchless projects.
One key trend is the increasing use of robotics and automation in trenchless operations. Robotic systems can perform complex tasks with greater precision and speed than manual methods, reducing labor costs and improving safety. Automation also allows for more precise control over the installation process, leading to improved outcomes.
Materials Advancements
Materials science is also playing a significant role in the development of new trenchless technologies. Advanced materials such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and fiberglass-reinforced polymers (FRP) are being used to create pipes and liners with improved durability, flexibility, and corrosion resistance.
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE):HDPE pipes are lightweight, flexible, and highly resistant to corrosion and chemicals, making them ideal for a wide range of trenchless applications.
- Fiberglass-Reinforced Polymers (FRP):FRP pipes are strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant, offering excellent performance in challenging environments.
Trenchless Methods
New trenchless methods are also being developed to address specific challenges and applications. These methods include:
- Pipe Bursting:This method involves breaking an existing pipe and replacing it with a new one, all in a single operation.
- Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD):HDD is a versatile method that allows for the installation of pipes and cables underground without the need for excavation.
Last Point
In conclusion, trenchless technology has emerged as a game-changer in the infrastructure sector, offering a sustainable and cost-effective solution for various underground construction needs. Its ability to minimize environmental impact, reduce project timelines, and enhance safety makes it an indispensable tool for modern infrastructure development.
As the industry continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative applications of trenchless technology, shaping the future of infrastructure construction.
FAQ Explained: Trenchless Technology
What is trenchless technology?
Trenchless technology refers to a range of construction methods that allow for the installation, repair, or replacement of underground utilities without the need for extensive excavation.
What are the benefits of trenchless technology?
Trenchless technology offers numerous benefits, including reduced environmental impact, faster project completion, lower costs, and enhanced safety compared to traditional excavation methods.
What are the different types of trenchless technology?
There are various types of trenchless technology, including horizontal directional drilling, pipe bursting, microtunneling, and cured-in-place pipe lining, each with its own unique applications and advantages.
 wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY
wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY