Business systems service only payroll and inventory processes – In the realm of business systems, streamlining payroll and inventory processes stands as a cornerstone for organizational efficiency. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of these vital functions, exploring best practices, challenges, and the transformative benefits of integrating them for unparalleled business outcomes.
Payroll Processes

Payroll processing involves managing the payment of employee wages and benefits. It ensures that employees are paid accurately and on time, and that all relevant deductions and contributions are handled correctly.
Types of Payroll Processes
- Manual Payroll:Payroll calculations are performed manually, often using spreadsheets or calculators.
- Semi-Automated Payroll:Some aspects of payroll processing are automated, such as data entry or tax calculations, while others are still performed manually.
- Fully Automated Payroll:All aspects of payroll processing are automated, including data entry, calculations, and payments.
Payroll Calculations
Payroll calculations involve determining the amount of pay an employee is entitled to, after taking into account deductions and contributions. Common deductions include:
- Income tax
- Social security contributions
- Health insurance premiums
- Retirement contributions
Contributions include:
- 401(k) plans
- Health savings accounts
- Flexible spending accounts
Importance of Accurate Payroll Processing
Accurate payroll processing is crucial for:
- Compliance with Laws and Regulations:Failure to comply with payroll regulations can result in penalties and fines.
- Employee Satisfaction:Correct and timely payments boost employee morale and productivity.
- Business Reputation:Accurate payroll processing demonstrates a responsible and trustworthy business.
Inventory Processes
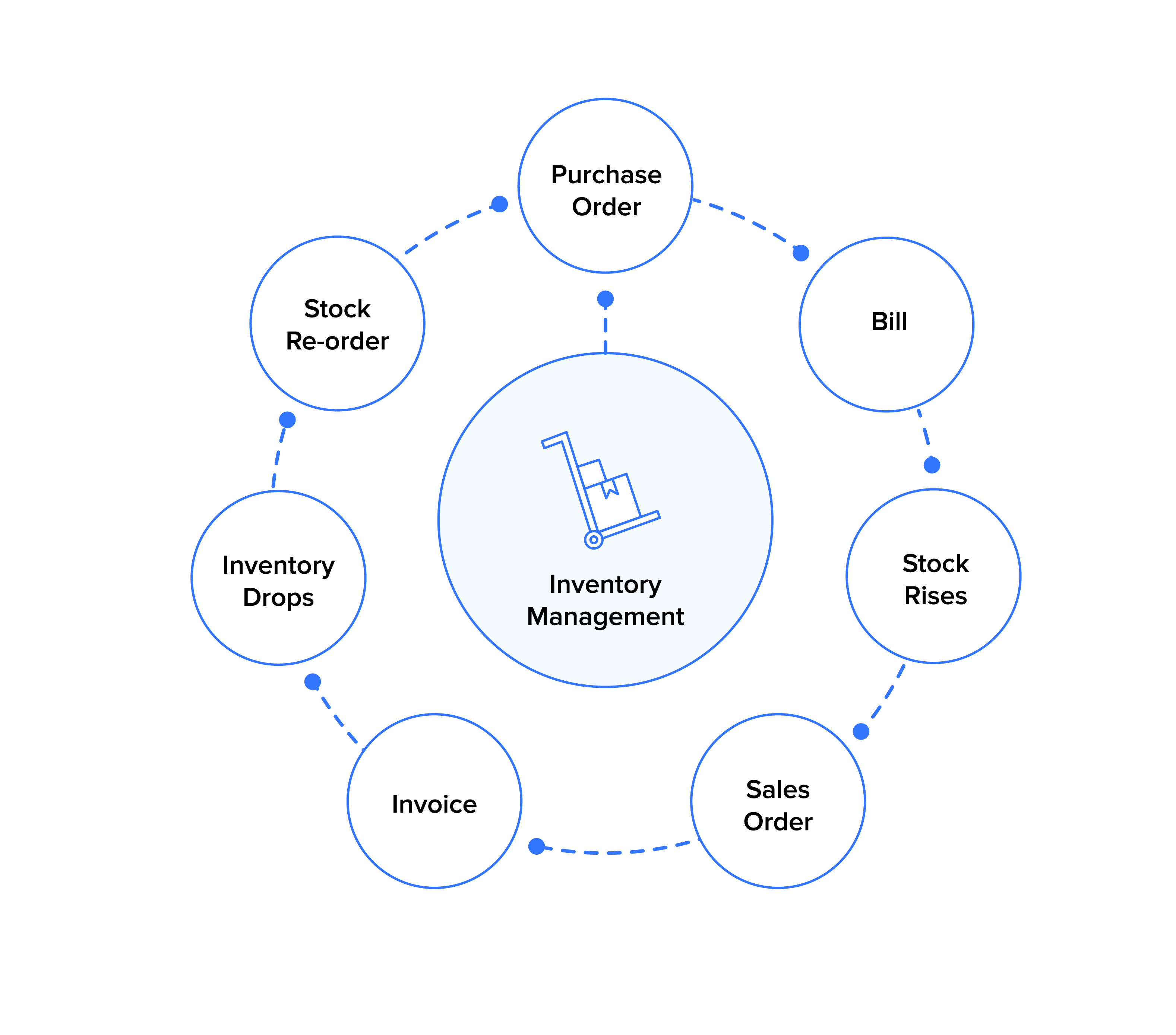
Inventory management plays a crucial role in optimizing business operations and profitability. It involves controlling the flow of goods from the point of acquisition to the point of sale or consumption. Effective inventory management techniques ensure that businesses have the right amount of inventory to meet customer demand while minimizing waste and costs.
There are several inventory management techniques that businesses can implement based on their specific needs and industry. Some of the most common techniques include:
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory:JIT aims to minimize inventory by ordering goods only when they are needed for production or sale. This technique reduces storage costs and the risk of obsolete inventory.
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO):FIFO assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first. This method helps prevent spoilage and ensures that inventory is used in the order it was acquired.
- Last-In, First-Out (LIFO):LIFO assumes that the most recently acquired inventory is sold first. This method can be beneficial for businesses that expect inflation, as it reduces the cost of goods sold and increases profits.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ):EOQ is a mathematical formula that helps businesses determine the optimal quantity of inventory to order at a time. EOQ considers factors such as demand, holding costs, and ordering costs.
- Safety Stock:Safety stock is an additional amount of inventory held to buffer against unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply.
Step-by-Step Guide to Inventory Management
Effective inventory management requires a systematic approach. Here is a step-by-step guide to help businesses implement a robust inventory management system:
- Establish Inventory Goals:Determine the specific goals of inventory management, such as reducing costs, improving customer service, or increasing profitability.
- Forecast Demand:Forecast future demand for inventory based on historical data, market trends, and customer behavior.
- Set Inventory Levels:Determine the appropriate inventory levels for each item, considering factors such as demand, lead time, and safety stock.
- Implement Inventory Management Software:Use inventory management software to automate tasks, track inventory levels, and generate reports.
- Monitor Inventory Regularly:Monitor inventory levels on a regular basis to identify any discrepancies or potential issues.
- Adjust Inventory Levels as Needed:Adjust inventory levels based on changes in demand, supply, or other factors.
- Conduct Inventory Audits:Conduct periodic inventory audits to verify the accuracy of inventory records.
Benefits of Effective Inventory Management
Effective inventory management offers numerous benefits to businesses, including:
- Reduced Costs:Minimizing inventory levels reduces storage costs, insurance costs, and the risk of obsolete inventory.
- Improved Customer Service:Having the right amount of inventory on hand ensures that customers can get the products they need when they need them.
- Increased Profitability:Effective inventory management helps businesses optimize their inventory investment, leading to increased profitability.
- Enhanced Efficiency:Automated inventory management systems streamline processes, saving time and reducing errors.
- Improved Decision-Making:Accurate inventory data provides valuable insights for making informed business decisions.
Integration of Payroll and Inventory Processes
Integrating payroll and inventory processes involves connecting the systems and data used to manage these functions, enabling the seamless flow of information between them. This integration can enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and provide valuable insights for businesses.
Benefits of Integrating Payroll and Inventory Processes
- Improved accuracy: Automating data transfer between payroll and inventory systems eliminates manual data entry, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring consistency.
- Increased efficiency: Integration streamlines processes, saving time and resources by eliminating the need for manual reconciliation and data duplication.
- Enhanced visibility: A centralized platform provides a comprehensive view of both payroll and inventory data, enabling better decision-making and resource allocation.
- Cost savings: By automating tasks and reducing errors, businesses can save on labor costs and minimize expenses associated with payroll and inventory management.
Examples of Successful Integration
- Retail:Large retail chains have integrated payroll and inventory systems to manage employee schedules based on inventory levels, ensuring optimal staffing during peak periods.
- Manufacturing:Manufacturers have integrated these systems to track labor costs associated with specific production batches, providing insights into production efficiency and profitability.
Challenges of Managing Business Systems

Managing business systems is a complex task that comes with a unique set of challenges. These challenges can stem from a variety of factors, including the size and complexity of the system, the number of users, and the availability of resources.
Common challenges include:
- Integration:Integrating different business systems can be a complex and time-consuming process. This is especially true when the systems are from different vendors or use different technologies.
- Data management:Managing data across multiple systems can be a challenge. This is especially true when the data is sensitive or needs to be kept confidential.
- Security:Ensuring the security of business systems is essential. This is especially true in today’s environment, where cyberattacks are becoming increasingly common.
- Cost:Implementing and maintaining business systems can be expensive. This is especially true for large and complex systems.
- Training:Training users on how to use business systems can be a challenge. This is especially true for complex systems.
There are a number of strategies that can be used to overcome these challenges. These strategies include:
- Planning:Careful planning is essential for successful business systems management. This includes identifying the goals of the system, the users who will be using it, and the resources that will be needed.
- Communication:Clear and concise communication is essential for successful business systems management. This includes communicating with users, vendors, and other stakeholders.
- Training:Training users on how to use business systems is essential for successful business systems management. This includes providing training on the system’s functionality, security features, and best practices.
- Monitoring:Monitoring business systems is essential for successful business systems management. This includes monitoring the system’s performance, security, and usage.
- Continuous improvement:Continuous improvement is essential for successful business systems management. This includes regularly reviewing the system’s performance and making improvements as needed.
Continuous improvement is essential for successful business systems management. This includes regularly reviewing the system’s performance and making improvements as needed. Continuous improvement can help to ensure that the system is meeting the needs of the business and that it is operating at peak efficiency.
Case Studies of Successful Business Systems Implementations
Businesses across various industries have successfully implemented business systems to enhance their operations. These case studies provide valuable insights into the factors that contribute to successful implementations and offer recommendations for businesses seeking to embark on similar initiatives.
A common thread among successful implementations is the involvement of stakeholders throughout the process. From the initial planning stages to the post-implementation evaluation, engaging key users and decision-makers ensures that the system aligns with the business’s objectives and needs.
Key Factors Contributing to Success, Business systems service only payroll and inventory processes
- Clear definition of business requirements and objectives
- Involvement of stakeholders throughout the process
- Selection of a suitable business system that meets specific needs
- Adequate training and support for users
- Regular monitoring and evaluation to ensure ongoing effectiveness
Recommendations for Successful Implementations
- Conduct a thorough assessment of business needs and objectives
- Involve key stakeholders in all phases of the implementation
- Choose a business system that aligns with the business’s size, industry, and requirements
- Provide comprehensive training and support to users
- Establish a governance structure to monitor and evaluate the system’s performance
Emerging Trends in Business Systems
The business landscape is constantly evolving, and with it, the systems that businesses use to operate. Emerging trends in business systems technology are having a major impact on how businesses operate, and these trends are expected to continue to shape the future of business systems.
One of the most significant trends in business systems technology is the rise of cloud computing. Cloud computing allows businesses to access software and data over the internet, rather than having to install and maintain it on their own servers.
This has a number of advantages, including reduced costs, increased flexibility, and improved security.
Another major trend is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) in business systems. AI can be used to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide insights into data. This can lead to increased efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
Finally, there is a growing trend towards the integration of business systems. This means that different systems, such as CRM, ERP, and HR, are being integrated to share data and functionality. This can lead to improved collaboration, reduced costs, and better decision-making.
Impact on Businesses
The emerging trends in business systems technology are having a major impact on businesses. These trends are helping businesses to become more efficient, productive, and profitable. They are also helping businesses to make better decisions and to respond more quickly to changes in the market.
Future of Business Systems
The future of business systems is bright. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and disruptive technologies emerge. These technologies will continue to shape the way that businesses operate, and they will help businesses to achieve even greater success.
Concluding Remarks
As we conclude our exploration of business systems service only payroll and inventory processes, it is evident that these functions are not mere tasks but strategic levers for driving operational excellence. By embracing a holistic approach, businesses can unlock the full potential of their systems, fostering a seamless flow of information and empowering decision-makers with real-time insights.
The journey towards business transformation begins with mastering these essential processes, setting the stage for continued growth and prosperity.
General Inquiries: Business Systems Service Only Payroll And Inventory Processes
What are the key benefits of integrating payroll and inventory processes?
Integrating payroll and inventory processes streamlines operations, reduces errors, improves data accuracy, enhances decision-making, and optimizes resource allocation.
How can businesses overcome the challenges of managing business systems?
Overcoming business systems management challenges requires a proactive approach, including regular system updates, staff training, data security measures, and continuous process improvement.
 wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY
wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY