Business specialist logistics inventory distribution transportation salary – Delving into the multifaceted world of business specialist logistics, we uncover the intricate interplay of inventory management, distribution, and transportation. From understanding the role and responsibilities of these specialists to exploring industry trends and career paths, this comprehensive guide sheds light on the complexities and rewards of this dynamic field.
Unveiling the secrets of inventory management, we delve into best practices, unravel the nuances of inventory systems, and reveal strategies for optimizing inventory levels. Distribution and transportation take center stage as we navigate the diverse modes of transportation, delve into channel selection, and uncover tips for maximizing efficiency.
Business Specialist Logistics Overview
Business Specialists in Logistics play a crucial role in managing the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. They work closely with various stakeholders, including manufacturers, distributors, and transportation providers, to ensure efficient and cost-effective logistics operations.
The logistics industry is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, globalization, and changing consumer demands. Business Specialists in Logistics must stay abreast of these trends to optimize supply chains and meet the needs of their clients.
Key Responsibilities, Business specialist logistics inventory distribution transportation salary
- Analyze logistics operations to identify areas for improvement
- Develop and implement strategies to enhance efficiency and reduce costs
- Manage relationships with suppliers, carriers, and other logistics providers
- Monitor industry trends and best practices to stay informed about the latest developments
- Provide consulting services to clients on logistics-related matters
Industry Landscape
The logistics industry is a global, multi-trillion-dollar sector that plays a vital role in the global economy. It encompasses various modes of transportation, including road, rail, air, and sea, as well as warehousing, distribution, and other related services.
Key trends in the logistics industry include:
- Increasing use of technology to automate processes and improve efficiency
- Growth of e-commerce and the need for fast and reliable delivery services
- Globalization and the need for efficient cross-border logistics solutions
- Sustainability and the focus on reducing environmental impact
Inventory Management

Inventory management is the backbone of any successful logistics and distribution operation. It ensures that the right products are available in the right quantities, at the right time, and at the right place. By optimizing inventory levels, businesses can reduce waste, improve customer service, and increase profitability.There are a number of different inventory management systems available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
The most common types of inventory systems include:
- Periodic inventory systems: These systems track inventory levels on a periodic basis, such as monthly or quarterly. They are relatively simple to implement and maintain, but they can be less accurate than other types of systems.
- Perpetual inventory systems: These systems track inventory levels in real time. They are more accurate than periodic inventory systems, but they can be more complex to implement and maintain.
- Hybrid inventory systems: These systems combine elements of both periodic and perpetual inventory systems. They offer a balance of accuracy and ease of implementation.
The best inventory management system for a particular business will depend on a number of factors, including the size of the business, the types of products it sells, and the volume of inventory it carries.In addition to choosing the right inventory management system, businesses can also implement a number of strategies to optimize inventory levels and reduce waste.
These strategies include:
- Using inventory forecasting to predict future demand.
- Establishing safety stock levels to buffer against unexpected fluctuations in demand.
- Implementing just-in-time (JIT) inventory management to reduce inventory carrying costs.
- Using vendor-managed inventory (VMI) to allow suppliers to manage inventory levels on behalf of the business.
By implementing effective inventory management practices, businesses can improve their overall efficiency and profitability.
Distribution and Transportation
Effective distribution and transportation are crucial for businesses to deliver products to customers efficiently and cost-effectively. Various modes of transportation, each with its advantages and disadvantages, are used in logistics.
The selection of an appropriate distribution channel depends on factors such as product characteristics, customer location, and cost considerations. Optimizing distribution and transportation efficiency involves careful planning and coordination, considering factors like route optimization, inventory management, and customer service levels.
Modes of Transportation
The choice of transportation mode depends on factors like cost, speed, reliability, and product characteristics.
- Road transportation:Trucks are widely used for short-distance and regional deliveries, offering flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
- Rail transportation:Trains are suitable for long-distance, high-volume shipments, providing cost efficiency and reliability.
- Air transportation:Airplanes are used for urgent or time-sensitive deliveries, despite being more expensive than other modes.
- Water transportation:Ships are used for international shipments, offering cost-effectiveness for bulky or heavy goods.
Distribution Channel Selection
Choosing the right distribution channel is crucial for efficient product delivery.
- Direct distribution:Selling directly to customers, eliminating intermediaries and providing greater control over distribution.
- Indirect distribution:Using intermediaries like wholesalers or retailers to reach customers, reducing distribution costs but sacrificing some control.
- Multi-channel distribution:Combining direct and indirect channels to reach customers through various touchpoints, increasing market reach.
Optimizing Distribution and Transportation Efficiency
Optimizing distribution and transportation processes improves efficiency and reduces costs.
- Route optimization:Using technology to plan efficient delivery routes, minimizing travel time and fuel consumption.
- Inventory management:Maintaining optimal inventory levels to avoid stockouts or excess inventory, ensuring product availability and minimizing storage costs.
- Customer service:Providing real-time tracking, timely delivery, and responsive customer support to enhance customer satisfaction.
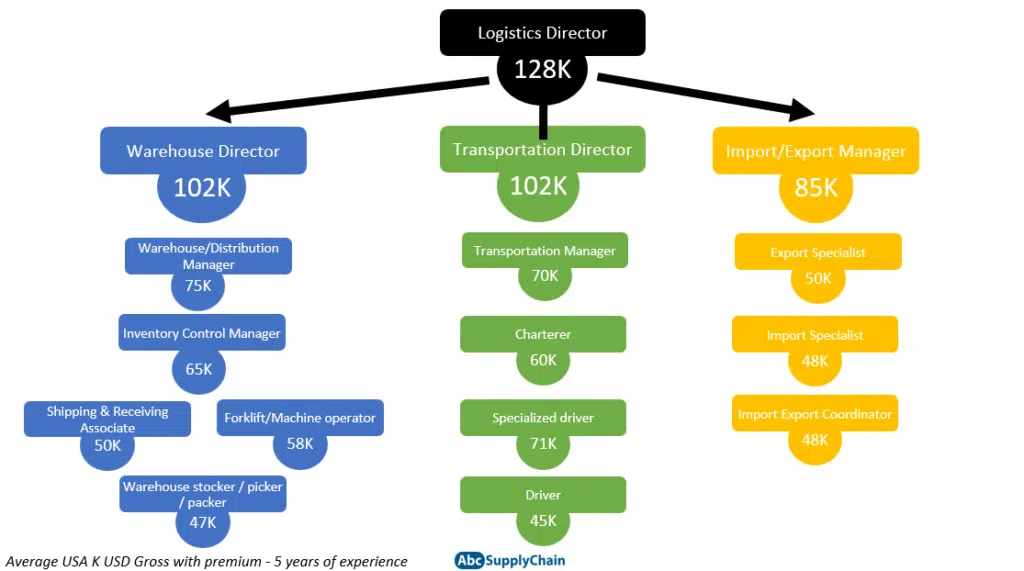
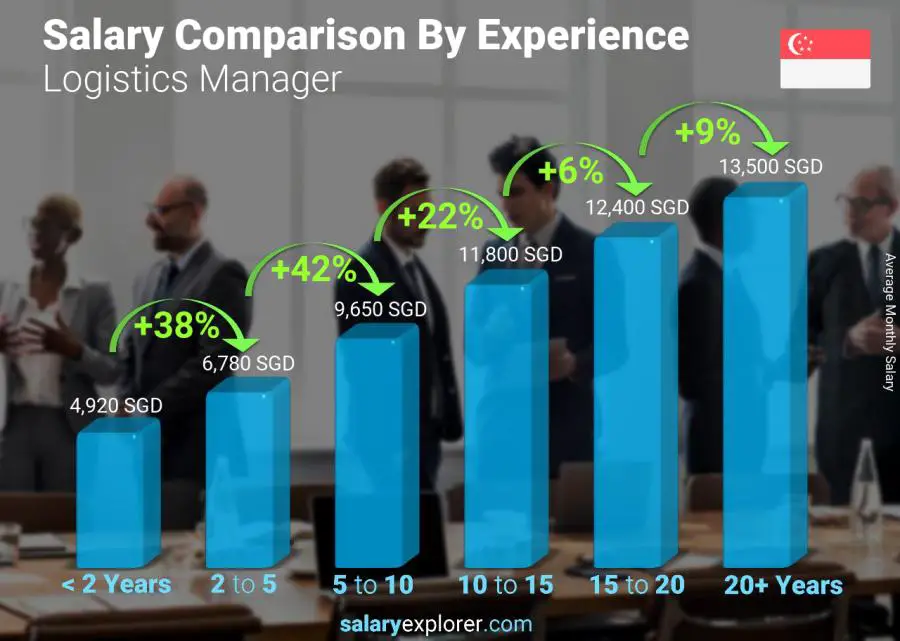
Salary and Career Path

Business Specialists in Logistics enjoy competitive salaries commensurate with their expertise and experience. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for Logistics Specialists was $76,270 in May 2021. The lowest 10 percent earned less than $43,920, and the highest 10 percent earned more than $127,590.
Career Path
Business Specialists in Logistics often start their careers as entry-level inventory or logistics coordinators. With experience and additional training, they can advance to roles such as logistics manager, supply chain manager, or operations manager. Some Business Specialists in Logistics may also choose to start their own consulting or logistics businesses.
Negotiating Salary and Benefits
When negotiating salary and benefits, it is important to be prepared. Research industry benchmarks to determine what similar professionals are earning. Be prepared to discuss your skills, experience, and accomplishments. You should also be prepared to negotiate other benefits, such as vacation time, sick leave, and retirement plans.
Last Word
As we conclude our exploration of business specialist logistics, we recognize the crucial role these professionals play in the seamless flow of goods and services. Their expertise in inventory management, distribution, and transportation ensures that businesses operate efficiently, reduce costs, and meet customer demands.
With a promising career path and competitive salary expectations, this field offers ample opportunities for growth and advancement.
FAQ Insights: Business Specialist Logistics Inventory Distribution Transportation Salary
What are the key responsibilities of a business specialist in logistics?
Business specialists in logistics oversee the efficient movement of goods and services, managing inventory, coordinating transportation, and ensuring timely delivery.
What are the different types of inventory systems used in logistics?
Common inventory systems include periodic inventory systems, perpetual inventory systems, and just-in-time inventory systems.
What factors should be considered when selecting a distribution channel?
Factors to consider include cost, speed, reliability, flexibility, and customer service.
What is the average salary range for business specialists in logistics?
Salary expectations vary based on experience, location, and industry, but typically range from $60,000 to $100,000 per year.
 wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY
wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY