Business personal property return where do you minus inventory – In the realm of business taxation, the Business Personal Property Return (BPPR) holds a pivotal role. This document serves as a crucial tool for businesses to report their personal property and claim deductions that can significantly impact their tax liability.
One key aspect of the BPPR is understanding how inventory affects these deductions.
Inventory, as it pertains to the BPPR, refers to the stock of goods a business holds for sale or use in its operations. The inclusion or exclusion of inventory in the BPPR can have a substantial effect on the amount of deductions a business can claim.
This article delves into the intricacies of inventory deductions in the BPPR, providing clarity and guidance for businesses seeking to navigate this aspect of their tax obligations.
Business Personal Property Return

A Business Personal Property Return (BPPR) is a tax form filed by businesses to report the personal property used in their operations. This information is used by local governments to assess property taxes.
The BPPR typically includes the following information:
- The name and address of the business
- A description of the personal property
- The cost or value of the personal property
- The location of the personal property
Inventory
Inventory is a critical aspect of a Business Personal Property Return (BPPR) as it represents the stock of goods and materials held by a business for sale or use in the production of goods or services. Accurate reporting of inventory is essential for determining the value of a business’s personal property and calculating its tax liability.
For the purpose of a BPPR, inventory includes:
- Raw materials and components
- Work in progress
- Finished goods
- Supplies
It’s important to note that inventory does not include:
- Real estate
- Vehicles
- Furniture and fixtures
- Intangible assets
Deductions

Deductions on a Business Personal Property Return (BPPR) reduce the amount of taxable personal property, thereby lowering the tax liability. Several types of deductions are commonly claimed by businesses, and it’s crucial to understand these deductions to maximize tax savings.
Types of Deductions
- Depreciation:Deduction for the wear and tear of property used in business operations.
- Depletion:Deduction for the extraction of natural resources, such as oil or minerals.
- Casualty and theft losses:Deduction for property lost or damaged due to events like fire, theft, or vandalism.
- Obsolescence:Deduction for property that has become obsolete or unusable due to technological advancements.
- Abandoned property:Deduction for property that has been discarded or abandoned.
Commonly Claimed Deductions
- Office equipment:Computers, desks, chairs, and other office supplies can be depreciated over their useful life.
- Vehicles:Business vehicles can be depreciated or deducted as a casualty loss if damaged or stolen.
- Machinery and equipment:Industrial machinery and equipment used in manufacturing or production can be depreciated.
- Inventory losses:Losses due to theft, spoilage, or obsolescence can be deducted.
- Bad debts:Uncollectible business debts can be deducted as a casualty loss.
Tax Implications
Filing a Business Personal Property Return (BPPR) has significant tax implications for businesses. Understanding these implications is crucial to ensure compliance and avoid potential penalties.
Properly reporting business personal property ensures accurate assessment of property taxes. Underreporting can result in underpayment of taxes, leading to penalties and interest charges. Conversely, overreporting can lead to an overpayment of taxes, which can be financially burdensome.
Penalties for Underreporting
- Fines and penalties imposed by tax authorities
- Interest charges on unpaid taxes
- Potential criminal charges in severe cases
Consequences of Overreporting
- Unnecessary financial burden due to overpayment of taxes
- Potential difficulty in obtaining refunds or credits
- Increased risk of audits and scrutiny by tax authorities
Filing Procedures: Business Personal Property Return Where Do You Minus Inventory
Filing a Business Personal Property Return (BPPR) is a legal requirement for businesses that own or use personal property in a given jurisdiction. The process involves submitting a form to the relevant tax authority, which provides details about the business’s personal property and its value.
Filing a BPPR is crucial for businesses to ensure compliance with tax laws and avoid penalties. Here are the step-by-step instructions on how to file a BPPR:
Filing Deadlines
The filing deadlines for BPPRs vary depending on the jurisdiction. It is important to check with the local tax authority to determine the specific deadline for your business. Failure to file by the deadline may result in penalties.
Filing Methods
BPPRs can be filed online, by mail, or in person. The availability of online filing may vary depending on the jurisdiction. It is recommended to check with the local tax authority for the preferred filing method.
Required Documentation
When filing a BPPR, businesses are required to provide certain documentation to support the information provided on the form. This documentation may include:
- A list of all personal property owned or used by the business
- The original cost or fair market value of each item of property
- The date the property was acquired
- The location of the property
Common Errors
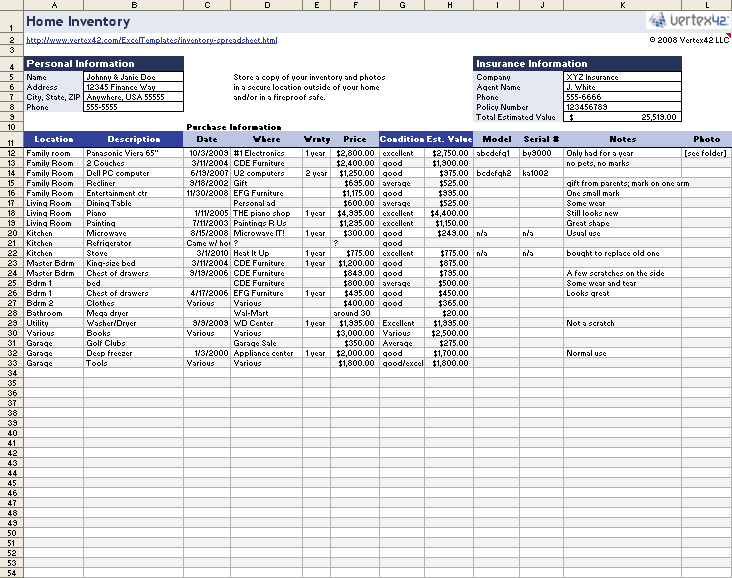
Inaccurate or incomplete information provided can lead to incorrect tax assessments and potential penalties. Avoiding these errors ensures a smooth filing process and accurate tax liability determination.
Common errors made when filing a BPPR include:
Incorrect Property Description, Business personal property return where do you minus inventory
- Failing to provide a detailed description of the property, including its make, model, serial number, and acquisition date.
- Inaccurately reporting the property’s condition or value.
Incorrect Ownership Information
- Mistakenly reporting the owner’s name, address, or taxpayer identification number.
- Failing to disclose any changes in ownership or use of the property during the tax year.
Incorrect Valuation
- Using an incorrect method to determine the property’s value.
- Failing to consider depreciation or other factors that may affect the property’s value.
Incorrect Exemptions or Deductions
- Claiming exemptions or deductions that do not apply to the property.
- Failing to provide supporting documentation for claimed exemptions or deductions.
Late Filing
- Missing the filing deadline, which can result in penalties and interest charges.
Closing Notes
Understanding the nuances of inventory deductions in the Business Personal Property Return is essential for businesses seeking to optimize their tax savings. By carefully considering the types of inventory that should be included or excluded, as well as the various deductions available, businesses can ensure they are fulfilling their tax obligations while minimizing their tax burden.
The information provided in this article serves as a valuable resource for businesses seeking to gain a comprehensive understanding of this complex topic.
Questions Often Asked
What types of inventory are included in the BPPR?
Inventory included in the BPPR generally includes raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods held for sale or use in the business.
How does inventory affect deductions on the BPPR?
Inventory can reduce the amount of deductions a business can claim on the BPPR because it is considered an asset. The value of inventory is deducted from the total value of personal property before deductions are calculated.
What are some common deductions that can be claimed on the BPPR?
Common deductions claimed on the BPPR include depreciation, repairs and maintenance, and insurance expenses related to business personal property.
 wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY
wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY