Business inventory tax is a crucial aspect of tax compliance for businesses that maintain inventory. Understanding its intricacies is essential to ensure accurate reporting and avoid penalties. This guide delves into the fundamentals of business inventory tax, including its types, calculations, exemptions, reporting requirements, and potential consequences for non-compliance.
Navigating the complexities of business inventory tax can be challenging, but with the right knowledge, businesses can effectively manage their tax obligations while minimizing the risk of errors or penalties. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the topic, empowering business owners to make informed decisions and maintain compliance.
Business Inventory Tax Basics
Business inventory tax is a levy imposed on the value of goods held by businesses for sale or use in the production of goods or services. Its primary purpose is to generate revenue for local governments.
There are various types of business inventory tax, including:
- Ad valorem tax: Based on the assessed value of the inventory.
- Specific tax: A flat rate per unit of inventory.
- Use tax: Levied on inventory used or consumed in the business.
Examples of items subject to business inventory tax include:
- Raw materials
- Work-in-progress
- Finished goods
- Supplies
Business Inventory Tax Calculations

Calculating business inventory tax involves determining the taxable value of the inventory and applying the appropriate tax rate. Several methods are used for this calculation, and the specific method employed may vary depending on the jurisdiction and the type of inventory.
The most common methods for calculating business inventory tax include:
Cost Method
Under the cost method, the taxable value of the inventory is based on the cost of the goods purchased. This method is straightforward and easy to implement, but it can result in over- or under-taxation if the cost of the goods does not accurately reflect their market value.
Market Value Method
The market value method uses the current market value of the inventory to determine its taxable value. This method provides a more accurate assessment of the inventory’s worth, but it can be more difficult to determine the market value of certain types of inventory.
Weighted Average Cost Method
The weighted average cost method calculates the taxable value of the inventory by taking the average cost of all the goods in the inventory. This method is more complex than the cost method but can provide a more accurate assessment of the inventory’s value.
Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) Method
The LIFO method assumes that the most recently purchased goods are the first to be sold. This method can result in lower taxable income during periods of inflation and higher taxable income during periods of deflation.
First-In, First-Out (FIFO) Method
The FIFO method assumes that the oldest goods in the inventory are the first to be sold. This method can result in higher taxable income during periods of inflation and lower taxable income during periods of deflation.
Business Inventory Tax Exemptions
Business inventory tax exemptions are a type of tax relief that can help businesses save money on their taxes. There are a number of different types of business inventory tax exemptions available, each with its own eligibility criteria.
Exempt Inventory
- Inventory held for sale in the ordinary course of business.
- Inventory used in the production of goods or services for sale.
- Inventory held for lease or rental.
Non-Exempt Inventory
- Inventory held for personal use.
- Inventory held for investment purposes.
- Inventory held for speculation.
Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible for a business inventory tax exemption, the inventory must meet the following criteria:
- It must be owned by the business.
- It must be held in the state where the business is located.
- It must be used in the business’s operations.
Examples of Businesses That Qualify for Business Inventory Tax Exemptions
Some examples of businesses that qualify for business inventory tax exemptions include:
- Retail stores
- Manufacturers
- Wholesalers
- Distributors
- Service businesses
Business Inventory Tax Reporting
Filing business inventory tax reports is crucial for businesses to meet their tax obligations accurately and timely. There are specific methods and timelines to adhere to, along with best practices to ensure accurate reporting.
Methods of Reporting Business Inventory Tax
Businesses can report their inventory tax using the following methods:
- Periodic Inventory Method:This method calculates inventory tax based on the inventory on hand at the end of the reporting period.
- Perpetual Inventory Method:This method tracks inventory levels continuously, updating the inventory records with each transaction. The inventory tax is calculated based on the inventory on hand at any given time.
Timeline for Business Inventory Tax Reporting
The timeline for business inventory tax reporting varies depending on the jurisdiction and tax regulations. However, common reporting periods include:
- Monthly:Some jurisdictions require businesses to file inventory tax reports on a monthly basis.
- Quarterly:Many jurisdictions require businesses to file inventory tax reports on a quarterly basis.
- Annually:Some jurisdictions require businesses to file inventory tax reports on an annual basis.
Tips for Accurate Business Inventory Tax Reporting
To ensure accurate business inventory tax reporting, consider the following tips:
- Maintain Accurate Inventory Records:Keep detailed records of all inventory items, including quantity, cost, and location.
- Reconcile Inventory Regularly:Regularly compare physical inventory counts with inventory records to identify any discrepancies.
- Use Inventory Management Software:Utilize inventory management software to automate inventory tracking and reporting.
- Consult with a Tax Professional:If needed, consult with a tax professional to ensure compliance with tax regulations and accurate reporting.
Business Inventory Tax Penalties
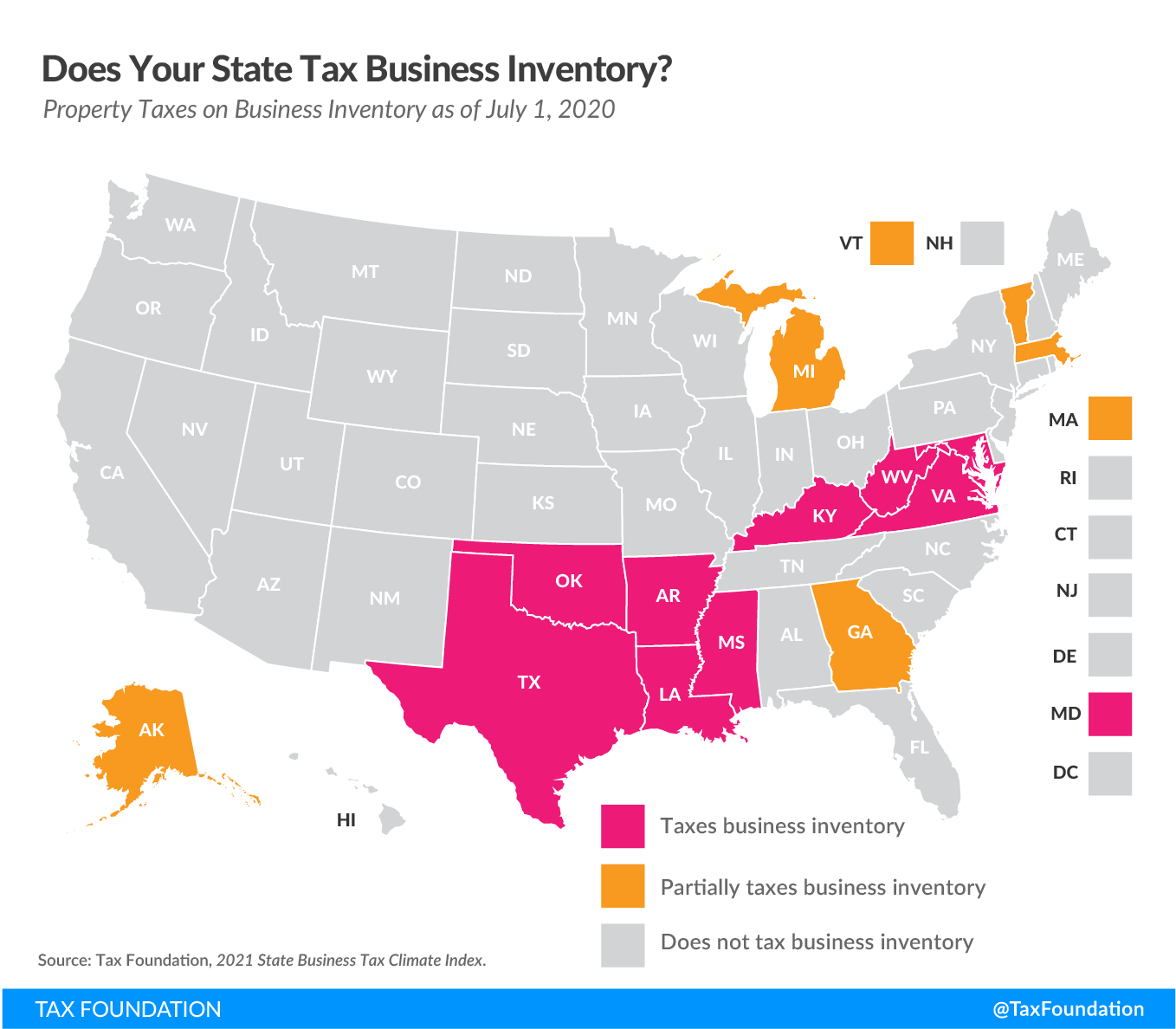
Businesses that fail to comply with business inventory tax laws may face penalties. These penalties can be significant, so it is important for businesses to be aware of their obligations and to take steps to comply with the law.
The penalties for failing to pay business inventory tax vary from state to state. In general, the penalties include:
- Late payment penalties
- Interest on unpaid taxes
- Fines
- Imprisonment
In addition to these penalties, businesses that fail to pay business inventory tax may also be subject to civil penalties. These penalties can include:
- Loss of business license
- Seizure of property
- Injunctions
Appealing Business Inventory Tax Penalties
Businesses that have been penalized for failing to pay business inventory tax may be able to appeal the penalties. The process for appealing business inventory tax penalties varies from state to state. In general, the process involves filing a petition with the state tax authority.
The petition must state the grounds for the appeal and must be supported by evidence.
The state tax authority will review the petition and make a decision on whether to grant the appeal. If the appeal is granted, the penalties may be reduced or eliminated.
Examples of Businesses that have been Penalized for Business Inventory Tax Violations
There are a number of businesses that have been penalized for business inventory tax violations. Some of the most notable examples include:
- In 2018, Walmart was fined $1 million for failing to pay business inventory tax in California.
- In 2019, Target was fined $500,000 for failing to pay business inventory tax in Texas.
- In 2020, Amazon was fined $250,000 for failing to pay business inventory tax in New York.
Last Word
In summary, business inventory tax is a significant consideration for businesses that hold inventory. By understanding the basics, businesses can accurately calculate their tax liability, take advantage of exemptions, and fulfill their reporting obligations. Failing to comply with business inventory tax regulations can result in penalties and legal consequences.
Therefore, it is essential for businesses to stay informed about the latest regulations and seek professional guidance when necessary to ensure compliance and avoid costly mistakes.
Quick FAQs
What is the purpose of business inventory tax?
Business inventory tax is a tax levied on the value of inventory held by businesses at the end of a taxable period. Its purpose is to generate revenue for local governments and support public services.
How is business inventory tax calculated?
The calculation method varies depending on the jurisdiction. Common methods include using the average monthly inventory value, the last day inventory value, or a combination of both.
Are there any exemptions to business inventory tax?
Yes, certain types of inventory may be exempt from business inventory tax, such as inventory held for resale, inventory in transit, and inventory used in manufacturing.
What are the penalties for failing to pay business inventory tax?
Penalties for non-compliance can include fines, interest charges, and even legal action. The severity of the penalties varies depending on the jurisdiction and the extent of the violation.
 wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY
wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY