Business inventory property tax is a crucial aspect of tax compliance for businesses holding inventory. Understanding the scope, valuation, exemptions, and strategies associated with this tax is essential to minimize liability and ensure compliance.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of business inventory property tax, providing a clear understanding of its implications and empowering businesses to make informed decisions.
Definition and Scope of Business Inventory Property Tax
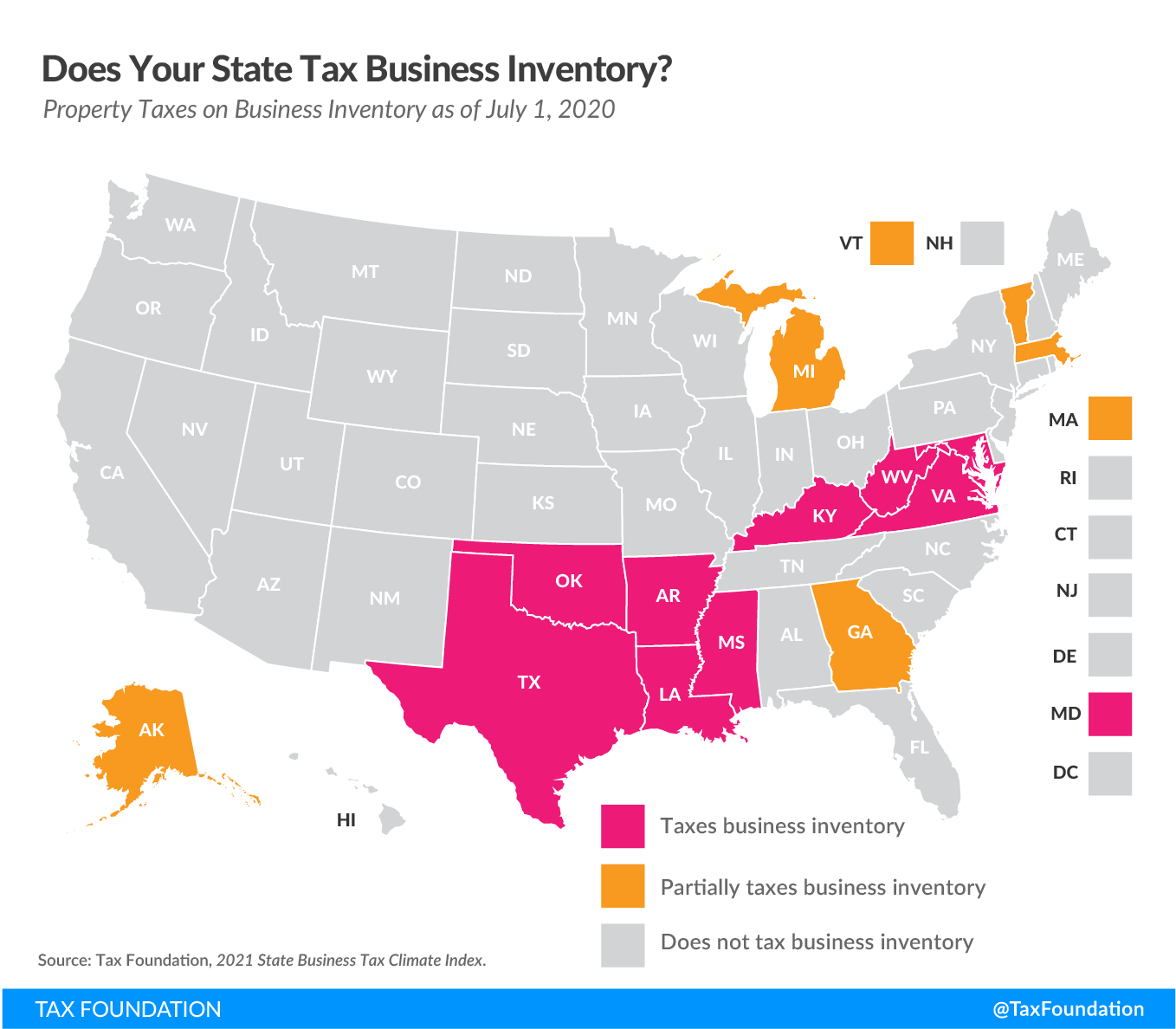
Business inventory property tax is a form of property tax levied on the value of inventory held by businesses.
Businesses subject to this tax include those that hold inventory for sale or use in the production of goods or services. The tax is typically assessed annually and is based on the average value of inventory held during the tax year.
Types of Inventory Subject to Taxation
The types of inventory subject to taxation vary by jurisdiction but generally include:
- Raw materials
- Work-in-progress
- Finished goods
- Supplies
Valuation of Business Inventory

Valuation of business inventory is a critical aspect of property tax assessment. The methods used to determine the value of inventory can significantly impact the tax liability of a business.
There are several common methods for valuing business inventory for tax purposes, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Cost Basis
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO):Assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first. This method can result in higher taxable income during periods of inflation.
- Last-In, First-Out (LIFO):Assumes that the most recently acquired inventory is sold first. This method can result in lower taxable income during periods of inflation.
- Weighted Average Cost:Calculates the average cost of inventory on hand based on the cost of all inventory acquired during a specific period.
Market Value
- Lower of Cost or Market (LCM):Compares the cost of inventory to its market value and uses the lower of the two for tax purposes.
- Retail Method:Uses the retail price of inventory to estimate its cost. This method is often used for retail businesses.
Impact of Valuation on Tax Liability
The choice of valuation method can have a significant impact on a business’s tax liability. For example, using LIFO during periods of inflation can result in lower taxable income and, therefore, lower taxes. Conversely, using FIFO during periods of inflation can result in higher taxable income and higher taxes.
Exemptions and Deductions: Business Inventory Property Tax
Businesses may qualify for exemptions or deductions that can reduce their business inventory property tax liability. Understanding these exemptions and deductions can help businesses save money on their tax bills.
Eligibility Criteria for Exemptions
- Agricultural products:Inventory held for agricultural purposes may be exempt from property tax in some jurisdictions.
- Inventory in transit:Inventory that is being shipped to or from a business may be exempt from property tax.
- Damaged or obsolete inventory:Inventory that is damaged or obsolete may be eligible for a deduction from its taxable value.
Impact of Exemptions and Deductions
Exemptions and deductions can significantly reduce a business’s property tax liability. By taking advantage of these exemptions and deductions, businesses can free up cash flow and reduce their overall tax burden.
Tax Assessment and Payment
Tax Assessment Process
The process of tax assessment for business inventory property tax typically involves the following steps:
- The tax authority sends out assessment notices to businesses that are required to file a business inventory property tax return.
- Businesses must review the assessment notice and make any necessary corrections or adjustments.
- The tax authority reviews the assessment and may make further adjustments based on the information provided by the business.
- The tax authority issues a final assessment notice to the business, which includes the amount of tax due.
Filing and Payment
Businesses must file their business inventory property tax return and pay the tax due by the deadline specified on the assessment notice. The following steps provide a general guide on how to file and pay the tax:
- Obtain the necessary forms from the tax authority’s website or office.
- Complete the forms accurately and submit them to the tax authority by the deadline.
- Make a payment for the amount of tax due by the deadline. The tax authority may offer various payment options, such as online payments, mail-in payments, or in-person payments.
Consequences of Late Filing or Non-Payment
Businesses that fail to file their business inventory property tax return or pay the tax due by the deadline may face consequences, which may include:
- Penalties and interest charges
- Legal action, such as a lawsuit
- Seizure of property
Tax Planning and Strategies
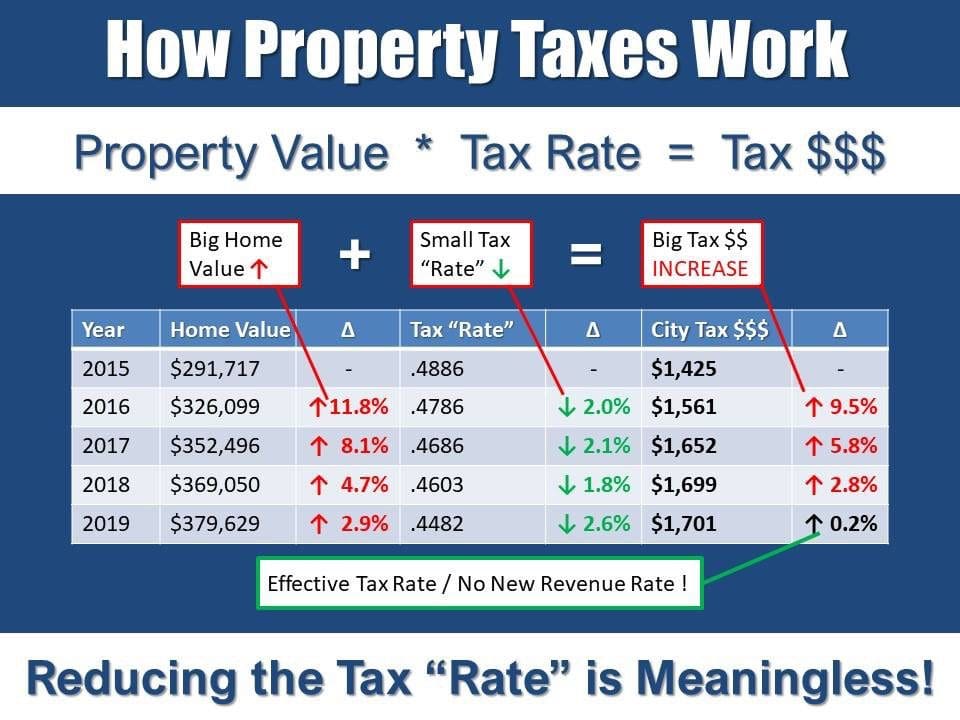
Tax planning is a crucial aspect of business inventory property tax management. It involves proactive measures to minimize tax liability while ensuring compliance with tax laws. By implementing effective tax planning strategies, businesses can optimize their financial position and improve profitability.
Benefits of Tax Planning, Business inventory property tax
* Reduced tax liability
- Improved cash flow
- Enhanced financial stability
- Increased investment opportunities
Effective Tax Planning Strategies
* Inventory Valuation:Choose appropriate inventory valuation methods that align with business objectives and minimize tax liability.
Exemptions and Deductions
Identify and utilize all applicable exemptions and deductions to reduce taxable inventory value.
Inventory Management
Implement efficient inventory management practices to reduce inventory levels and avoid overstocking.
Property Tax Appeals
If necessary, consider filing an appeal to contest the assessed value of business inventory.
Professional Tax Advice
Consult with tax professionals to obtain expert guidance on tax planning strategies and ensure compliance.
Final Summary
In summary, business inventory property tax is a complex but manageable aspect of tax compliance. By understanding the key concepts, valuation methods, exemptions, and strategies Artikeld in this guide, businesses can effectively manage their tax liability and stay compliant with regulations.
General Inquiries
What is business inventory property tax?
Business inventory property tax is a tax levied on the value of inventory held by businesses on a specific assessment date.
What types of businesses are subject to this tax?
Businesses that maintain inventory for sale or use in the ordinary course of their business are typically subject to business inventory property tax.
How is business inventory valued for tax purposes?
Business inventory is typically valued at its cost or market value, whichever is lower, as of the assessment date.
What exemptions are available for business inventory property tax?
Exemptions may vary by jurisdiction but commonly include exemptions for inventory held for resale, inventory in transit, and inventory damaged or destroyed.
What strategies can businesses use to minimize business inventory property tax liability?
Strategies to minimize liability include optimizing inventory levels, utilizing tax deductions and exemptions, and implementing effective tax planning strategies.
 wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY
wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY