Business inventory fiscal year tax property kentucky – In Kentucky, the topic of business inventory during the fiscal year has significant tax implications. This article will provide an overview of how the fiscal year affects business inventory, the property tax implications, and best practices for managing inventory to optimize tax outcomes.
Business Inventory Management in Kentucky
Managing business inventory in Kentucky is crucial for ensuring smooth operations and profitability. Kentucky’s strategic location and robust manufacturing sector make it essential for businesses to maintain efficient inventory systems.
Best practices for inventory management in Kentucky include:
- Centralized inventory system:Implementing a centralized inventory system allows businesses to track stock levels, manage orders, and optimize inventory allocation across multiple locations.
- Regular inventory audits:Conducting regular inventory audits helps identify discrepancies, prevent shrinkage, and ensure accurate stock records.
- Just-in-time inventory management:Adopting just-in-time inventory management techniques can minimize storage costs and reduce waste by receiving inventory only when needed.
Challenges of Inventory Management in Kentucky
Inventory management in Kentucky faces certain challenges, including:
- Seasonal fluctuations:Kentucky’s tourism industry and agricultural sector experience seasonal fluctuations, impacting inventory demand and storage requirements.
- Transportation costs:Kentucky’s location can lead to higher transportation costs for importing and exporting goods, affecting inventory management.
- Labor shortages:Kentucky’s manufacturing sector faces labor shortages, which can impact inventory handling and distribution.
Fiscal Year Considerations for Business Inventory in Kentucky
Kentucky’s fiscal year begins on July 1st and ends on June 30th. This is important for businesses to know because it affects how they account for their inventory for tax purposes. Businesses must use the same fiscal year for both state and federal tax purposes.
Tax Implications
The tax implications of business inventory during the fiscal year in Kentucky are as follows:
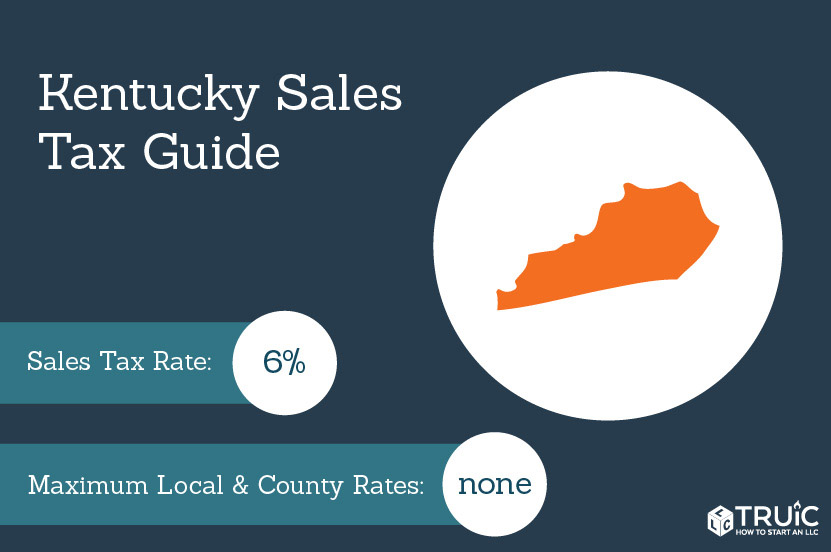
- Inventory is taxed at the rate of 6%.
- Businesses can deduct the cost of goods sold from their gross income.
- Businesses can also take a credit for the amount of sales tax they paid on inventory that was purchased during the fiscal year.
Property Tax Implications of Business Inventory in Kentucky
Business inventory is subject to property tax in Kentucky. The tax is based on the value of the inventory as of January 1 of each year. The tax rate varies depending on the county in which the business is located.
To calculate the property tax on business inventory, you will need to know the following:
- The value of your inventory as of January 1
- The property tax rate in your county
Once you have this information, you can calculate your property tax by multiplying the value of your inventory by the property tax rate.
Exemptions and Deductions
There are a number of exemptions and deductions available for business inventory property tax in Kentucky. These include:
- Inventory that is held for sale in the ordinary course of business
- Inventory that is stored in a public warehouse
- Inventory that is owned by a non-profit organization
If you qualify for any of these exemptions or deductions, you will need to file a form with the county clerk’s office.
Case Studies of Business Inventory Management in Kentucky

Businesses in Kentucky have employed various strategies to optimize their inventory management, resulting in improved efficiency, cost savings, and increased profitability. Let’s explore a few notable case studies:
Case Study 1
Company:XYZ Manufacturing Industry:Automotive Parts Manufacturing Strategy:Implemented a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system to reduce inventory levels and improve cash flow. Tactics:
- Established close relationships with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of materials.
- Implemented Kanban cards to signal the need for replenishment.
- Reduced lead times and increased production flexibility.
Results:
- Reduced inventory levels by 30%, freeing up capital for other investments.
- Improved cash flow by reducing inventory carrying costs.
- Increased production efficiency by eliminating overstocking and understocking.
Case Study 2, Business inventory fiscal year tax property kentucky
Company:ABC Distribution Industry:Wholesale Distribution Strategy:Adopted a radio frequency identification (RFID) system to enhance inventory accuracy and tracking. Tactics:
- Installed RFID tags on all inventory items.
- Implemented RFID readers throughout the warehouse.
- Automated inventory counting and tracking processes.
Results:
- Improved inventory accuracy to over 99%, reducing losses due to shrinkage and misplacement.
- Increased inventory turnover rate by optimizing stock levels.
- Reduced labor costs associated with manual inventory counting.
Best Practices for Managing Business Inventory in Kentucky
Managing business inventory in Kentucky effectively is crucial for optimizing operations and maximizing profitability. Here’s a comprehensive guide to best practices that businesses of all sizes can implement:
Inventory Tracking
Establishing a robust inventory tracking system is the cornerstone of effective inventory management. It provides real-time visibility into stock levels, allowing businesses to make informed decisions about replenishment and avoid stockouts. Consider using inventory management software or implementing a manual system that accurately tracks inventory levels, including quantities on hand, in transit, and on order.
Forecasting
Accurate forecasting is essential for anticipating demand and ensuring optimal inventory levels. Businesses should leverage historical data, industry trends, and market analysis to develop reliable forecasts. By effectively forecasting demand, businesses can minimize the risk of overstocking or understocking, leading to reduced costs and improved customer satisfaction.
Optimization
Inventory optimization involves finding the balance between holding sufficient stock to meet demand while minimizing carrying costs. Businesses should establish safety stock levels to buffer against unexpected fluctuations in demand and implement inventory control techniques, such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory management, to reduce inventory holding costs.
Collaboration
Effective inventory management requires collaboration between various departments within a business, including purchasing, sales, and operations. Open communication and information sharing ensure that all stakeholders have access to accurate inventory data and can make informed decisions.
Technology Utilization
Leveraging technology can significantly enhance inventory management efficiency. Businesses should consider implementing inventory management software that automates tasks, provides real-time data, and generates reports for analysis. Additionally, using barcode scanners and radio frequency identification (RFID) technology can streamline inventory tracking and improve accuracy.
Continuous Improvement
Inventory management is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement. Businesses should regularly review their inventory management practices, identify areas for optimization, and implement changes to enhance efficiency and effectiveness. By embracing a culture of continuous improvement, businesses can ensure that their inventory management practices remain aligned with changing business needs and industry best practices.
Final Review
By understanding the tax implications and implementing effective inventory management strategies, businesses in Kentucky can minimize their tax liability and optimize their financial performance.
Question Bank: Business Inventory Fiscal Year Tax Property Kentucky
What is the fiscal year in Kentucky?
The fiscal year in Kentucky runs from July 1st to June 30th.
How is business inventory taxed as property in Kentucky?
Business inventory is taxed as tangible personal property in Kentucky and is subject to the state’s property tax rate.
What exemptions and deductions are available for business inventory property tax in Kentucky?
There are several exemptions and deductions available for business inventory property tax in Kentucky, including the manufacturer’s inventory exemption and the agricultural inventory exemption.
 wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY
wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY