Business inventories macroeconomics problem – Delving into the intricate world of business inventories, we explore their pivotal role as a macroeconomic barometer, offering insights into the ebb and flow of economic activity. From their impact on GDP growth to their influence on inflation and interest rates, this comprehensive analysis unravels the complexities of inventory fluctuations and their far-reaching consequences.
Unveiling the strategies businesses employ to manage their inventories, we delve into the delicate balance between holding high or low inventory levels. Success stories from various industries showcase the transformative power of effective inventory management, while the role of technology in revolutionizing these practices is examined.
Business Inventories and Economic Indicators
Business inventories play a crucial role as leading indicators of economic activity, providing valuable insights into the overall health of the economy. Changes in inventory levels reflect businesses’ expectations about future demand and their production and sales plans.
Relationship with GDP Growth
A strong positive correlation exists between changes in business inventories and GDP growth. When businesses anticipate rising demand, they tend to increase their inventory levels to meet expected sales. This accumulation of inventories contributes positively to GDP growth.
Conversely, when businesses anticipate a slowdown in demand, they reduce their inventory levels. This destocking reduces GDP growth as the decrease in inventory investment offsets increases in other components of GDP.
Impact on Economic Forecasts
Changes in business inventories can significantly impact economic forecasts. Unexpectedly large increases or decreases in inventories can alter projections of future economic growth.
For instance, in 2008, a sharp decline in business inventories contributed to the severity of the financial crisis. Businesses had overestimated demand, resulting in excessive inventory levels. When demand plummeted, they were forced to liquidate inventories at a loss, exacerbating the economic downturn.
Macroeconomic Impact of Inventory Fluctuations

Inventory fluctuations can have a significant impact on the macroeconomic environment, influencing factors such as inflation, interest rates, and economic stability.
Inflation and Interest Rates
When businesses experience unexpected increases in inventory levels, they may be forced to reduce prices to clear excess stock. This can lead to deflationary pressures in the economy, lowering the overall price level and reducing inflation.
Conversely, if businesses underestimate demand and experience inventory shortages, they may increase prices to replenish their stock quickly. This can contribute to inflationary pressures, driving up the overall price level and increasing inflation.
Inventory fluctuations can also affect interest rates. When businesses hold excessive inventory, they may have less need to borrow money for investment or working capital. This can reduce demand for loans and put downward pressure on interest rates.
Economic Instability
Inventory imbalances can contribute to economic instability by creating disruptions in the supply chain and affecting business investment.
When businesses overestimate demand and accumulate excessive inventory, they may have to sell off excess stock at a loss or face storage costs. This can lead to losses, reduced profits, and decreased investment in other areas.
Conversely, if businesses underestimate demand and experience inventory shortages, they may have to scramble to replenish their stock, leading to production delays, lost sales, and reduced economic growth.
Historical Examples
Throughout history, inventory cycles have played a role in macroeconomic outcomes.
The Great Depression of the 1930s was partly caused by a buildup of unsold inventory in the late 1920s. When the stock market crashed in 1929, businesses were left with excessive inventory and reduced demand, leading to deflation and economic contraction.
More recently, the 2008 financial crisis was preceded by a surge in inventory accumulation in the housing market. When the housing bubble burst, businesses were left with unsold homes and other real estate assets, contributing to the financial crisis and subsequent recession.
Inventory Management Strategies
Inventory management strategies are critical for businesses to optimize their operations, reduce costs, and meet customer demand effectively. These strategies involve determining the appropriate inventory levels to hold, considering factors such as product demand, lead times, and storage costs.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
- Aims to minimize inventory levels by receiving goods only when needed for production or sale.
- Reduces storage costs, improves inventory turnover, and minimizes obsolescence.
- Requires close coordination with suppliers and efficient logistics systems.
- Suitable for industries with high product demand and short lead times, such as manufacturing and retail.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Model
- Determines the optimal quantity of inventory to order at a time to minimize total inventory costs.
- Considers factors such as order costs, holding costs, and demand rate.
- Helps businesses balance the trade-off between holding high inventory levels (higher holding costs) and placing frequent orders (higher order costs).
- Suitable for industries with stable demand and predictable lead times.
Safety Stock
- Additional inventory held to buffer against unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply.
- Prevents stockouts and ensures customer satisfaction.
- However, holding high safety stock levels can increase storage costs and reduce inventory turnover.
- Suitable for industries with unpredictable demand or long lead times.
Role of Technology in Inventory Management
Technology has significantly transformed inventory management practices, revolutionizing the way businesses track, manage, and optimize their inventory. From data analytics to automation, technological advancements have brought numerous benefits and challenges to inventory management.
Data Analytics, Business inventories macroeconomics problem
Data analytics plays a crucial role in inventory management. By leveraging data from various sources, businesses can gain valuable insights into their inventory patterns, demand forecasting, and supply chain performance. This data-driven approach enables businesses to:
- Identify trends and patterns in inventory levels
- Predict future demand more accurately
- Optimize inventory levels to minimize stockouts and overstocking
Automation
Automation has become increasingly prevalent in inventory management, streamlining processes and reducing manual labor. Automated systems can perform tasks such as:
- Tracking inventory levels in real-time
- Generating purchase orders and invoices
- Monitoring stock levels and triggering alerts for low inventory
Automation not only improves efficiency but also reduces human error, leading to more accurate and reliable inventory management.
Innovative Solutions
Technology has enabled the development of innovative inventory management solutions, including:
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID):RFID tags can track inventory items throughout the supply chain, providing real-time visibility into inventory levels.
- Blockchain:Blockchain technology can enhance inventory transparency and security, reducing the risk of fraud and theft.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of data to identify patterns, predict demand, and optimize inventory levels.
These technological advancements have revolutionized inventory management, empowering businesses to make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge.
Global Supply Chain and Inventory Management
Managing inventories in a global supply chain presents unique challenges due to the increased complexity and interconnectedness of the supply network. Coordinating inventory levels across multiple countries, time zones, and transportation modes requires careful planning and coordination.
International trade and logistics play a significant role in inventory management. Fluctuations in exchange rates, customs regulations, and transportation delays can impact inventory levels and lead to stockouts or overstocking.
Best Practices for Inventory Management in Global Supply Chains
- Centralized Inventory Management:Establish a central system to track inventory levels across all locations in the supply chain, providing real-time visibility and control.
- Safety Stock Optimization:Determine appropriate safety stock levels to mitigate risks associated with demand fluctuations and supply chain disruptions.
- Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI):Collaborate with suppliers to manage inventory levels based on demand forecasts, reducing the risk of stockouts and improving efficiency.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory Management:Minimize inventory levels by receiving goods only when needed, reducing storage costs and improving cash flow.
- Technology Adoption:Utilize inventory management software, RFID tracking, and data analytics to automate processes, improve accuracy, and enhance decision-making.
Inventory Financing and Capital Management
Inventory financing is a critical aspect of business operations, providing businesses with the necessary capital to maintain and manage their inventory levels. It enables businesses to purchase and store inventory without depleting their cash flow or tying up excessive capital in inventory.
There are various types of inventory financing available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Inventory financing can significantly impact capital management and profitability. By effectively managing inventory financing, businesses can optimize their working capital, reduce costs, and improve cash flow. Conversely, inefficient inventory financing can lead to increased carrying costs, reduced profitability, and financial distress.
Types of Inventory Financing
There are several types of inventory financing available to businesses, including:
- Line of credit:A revolving credit facility that allows businesses to borrow up to a pre-approved limit based on their creditworthiness.
- Inventory loan:A secured loan specifically designed to finance inventory purchases, with the inventory serving as collateral.
- Purchase order financing:A short-term loan that provides financing based on purchase orders, allowing businesses to purchase inventory before receiving payment from customers.
- Invoice factoring:A financing option where businesses sell their outstanding invoices to a factoring company at a discount, receiving immediate payment.
Sustainability and Inventory Management
Inventory management plays a significant role in promoting sustainability by reducing waste and conserving resources.
Environmental Impact of Inventory Accumulation
Accumulating excessive inventory can lead to several environmental impacts:
- Increased Carbon Emissions:Storing and transporting large amounts of inventory requires energy, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Waste Generation:Obsolete or damaged inventory often ends up in landfills, contributing to waste and pollution.
- Resource Depletion:Producing and storing inventory consumes raw materials, potentially depleting natural resources.
Role of Inventory Management in Reducing Waste and Promoting Sustainability
Effective inventory management practices can help mitigate these environmental impacts by:
- Optimizing Inventory Levels:Maintaining appropriate inventory levels reduces the risk of excess stock that may become obsolete or damaged.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory:JIT systems minimize inventory by ordering goods only when needed, reducing waste and storage costs.
- Reverse Logistics:Establishing efficient processes for returning and reusing obsolete or excess inventory helps reduce waste.
Sustainable Inventory Management Practices
Businesses can implement various sustainable inventory management practices, including:
- Using Sustainable Packaging:Opting for biodegradable or reusable packaging materials reduces environmental impact.
- Promoting Supplier Collaboration:Working closely with suppliers to optimize delivery schedules and reduce transportation emissions.
- Investing in Inventory Tracking Technology:Using technology to track inventory levels and identify obsolete stock helps reduce waste.
By adopting sustainable inventory management practices, businesses can minimize their environmental footprint while enhancing efficiency and reducing costs.
Inventory Optimization and Data Analysis
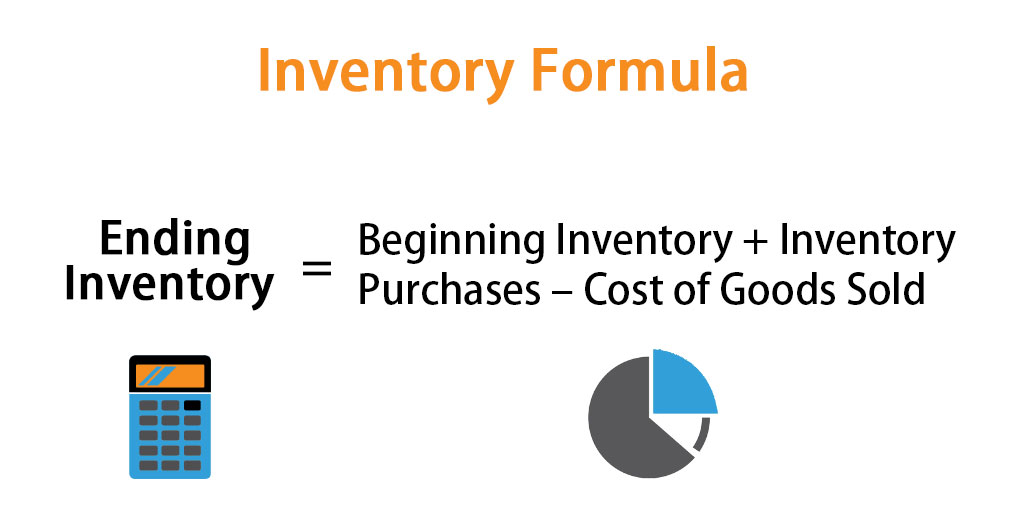
Inventory optimization is a critical aspect of business decision-making, enabling companies to determine the optimal levels of inventory to hold while minimizing costs and maximizing profitability. Data analytics and forecasting play a vital role in this process, providing valuable insights into demand patterns, supply chain dynamics, and other factors that influence inventory management.
Data Analytics in Inventory Management
- Predictive analytics can help forecast demand and anticipate future sales trends, enabling businesses to adjust inventory levels accordingly.
- Data mining can uncover hidden patterns and correlations in historical data, providing insights into customer behavior, product popularity, and seasonality.
- Machine learning algorithms can automate inventory optimization processes, making it more efficient and data-driven.
Benefits of Data-Driven Inventory Optimization
- Reduced inventory holding costs: By optimizing inventory levels, businesses can minimize the amount of inventory they hold, reducing storage, insurance, and handling costs.
- Improved customer service: Accurate inventory forecasting helps ensure that businesses have the right products in stock to meet customer demand, minimizing stockouts and backorders.
li>Increased profitability: By optimizing inventory levels, businesses can reduce waste and improve cash flow, leading to increased profitability.
Summary: Business Inventories Macroeconomics Problem

In closing, the intricate relationship between business inventories and macroeconomic outcomes underscores their significance in shaping economic landscapes. As we navigate the challenges of global supply chains and sustainability concerns, innovative inventory management practices emerge as key drivers of efficiency, profitability, and environmental stewardship.
Embracing data-driven optimization and leveraging technological advancements, businesses can harness the power of inventories to navigate economic complexities and fuel sustainable growth.
Common Queries
What are business inventories?
Business inventories refer to the stock of unsold finished goods, work-in-progress, and raw materials held by businesses.
How do business inventories impact economic growth?
Changes in business inventories can influence GDP growth, as an increase in inventories indicates a slowdown in demand, while a decrease suggests increased demand and economic expansion.
What are the different inventory management strategies?
Businesses can adopt various inventory management strategies, such as just-in-time (JIT), first-in, first-out (FIFO), or last-in, first-out (LIFO), depending on their specific needs and industry.
 wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY
wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY