Business inventories in economics play a pivotal role in shaping economic indicators and supply chain efficiency. From influencing GDP and employment to serving as an economic indicator, understanding inventory management strategies is crucial for businesses and economists alike.
This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of business inventories, their impact on economic indicators, and effective inventory management techniques. We’ll explore global trends, case studies, and real-world examples to provide a comprehensive understanding of this essential aspect of economic activity.
Business Inventories
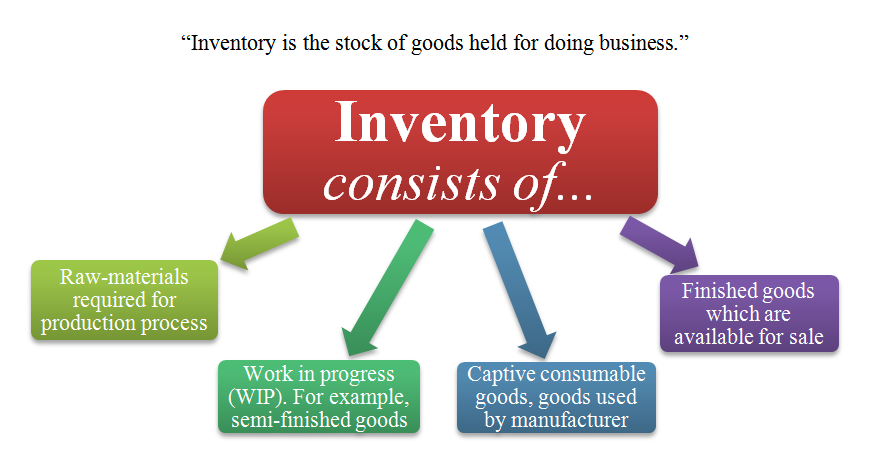
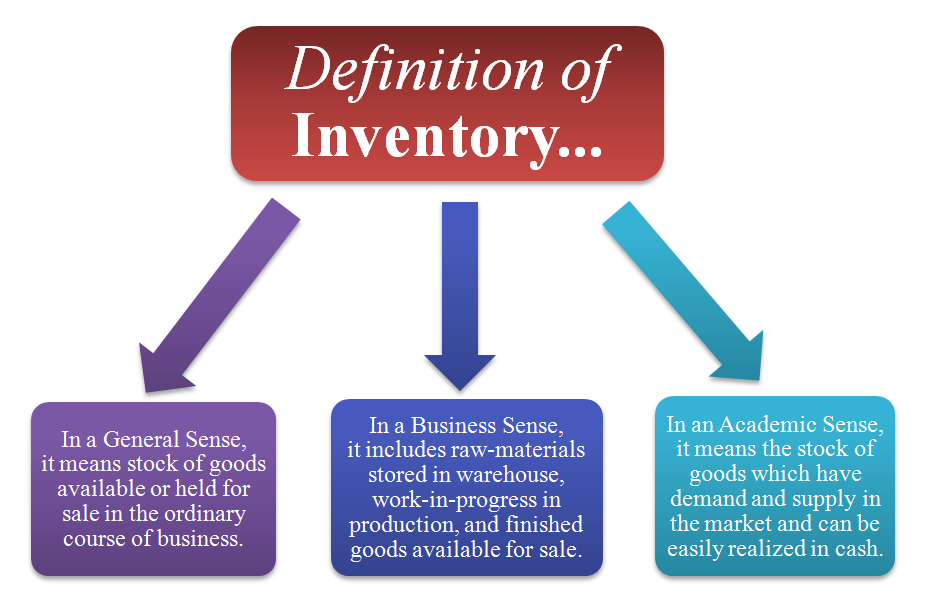
Business inventories refer to the stock of goods and materials held by businesses at various stages of production and distribution. These inventories play a crucial role in the smooth functioning of businesses and the overall economy.
Types of Inventories
There are several types of inventories, each serving a specific purpose:
- Raw Materials Inventory:Consists of raw materials used in the production process.
- Work-in-Progress Inventory:Refers to partially completed goods undergoing production.
- Finished Goods Inventory:Comprises completed products ready for sale to customers.
- Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) Inventory:Includes supplies used for maintaining and repairing equipment.
Managing Inventory Levels
Businesses must effectively manage inventory levels to optimize their operations and minimize costs. Some common inventory management techniques include:
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory:Minimizes inventory levels by receiving goods only when needed for production.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ):Determines the optimal quantity to order at a time to balance ordering costs and inventory holding costs.
- Safety Stock:Maintains a buffer of inventory to prevent stockouts during unexpected demand fluctuations.
Impact of Inventories on Economic Indicators
Business inventories play a significant role in shaping economic indicators, providing insights into the health and direction of the economy.
Relationship with Economic Growth
Inventory levels are closely tied to economic growth. When businesses anticipate increased demand, they tend to accumulate inventories to meet future orders. This increase in inventory investment contributes to overall economic growth, as it stimulates production and creates employment opportunities.
Conversely, when demand weakens, businesses may reduce their inventory levels to avoid holding excess stock. This decline in inventory investment can slow down economic growth.
Impact on GDP, Employment, and Inflation
Changes in business inventories can impact key economic indicators such as GDP, employment, and inflation.
- GDP:Inventory changes contribute to GDP growth or contraction. When businesses increase their inventories, it represents an increase in production, which adds to GDP. Conversely, when inventories decline, it indicates a slowdown in production, leading to a decrease in GDP.
- Employment:Changes in inventory levels can affect employment. When businesses anticipate higher demand and increase their inventories, they may hire additional workers to support production. Conversely, when inventory levels decline, businesses may reduce their workforce.
- Inflation:Inventory levels can influence inflation. When businesses hold excess inventory, they may be forced to sell at discounted prices to clear out stock. This can lead to lower prices and reduced inflationary pressures. Conversely, when inventories are low and demand is high, businesses may raise prices to replenish their stock, contributing to inflationary pressures.
Inventory Data as an Economic Indicator
Inventory data is widely used by economists and policymakers as an economic indicator. It provides valuable insights into business expectations, consumer demand, and the overall health of the economy.
Changes in inventory levels can signal potential shifts in economic activity. For example, a sudden increase in inventories may indicate that businesses are preparing for a period of strong demand, while a sharp decline may suggest a slowdown in economic growth.
Monitoring inventory data allows economists to track changes in business sentiment and anticipate future economic trends. It helps policymakers make informed decisions regarding monetary and fiscal policies to support economic stability and growth.
Inventory Management Strategies
Inventory management is crucial for businesses to optimize stock levels, minimize costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Various techniques are employed to manage inventories effectively.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
JIT aims to hold minimal inventory levels by producing goods only when there is customer demand. Benefits include reduced storage costs, improved cash flow, and increased flexibility. However, JIT requires reliable suppliers and efficient production processes to avoid stockouts.
Materials Requirement Planning (MRP)
MRP is a production planning and inventory control system that calculates the materials and components needed at specific times to meet production schedules. It helps ensure that materials are available when needed, reducing waste and production delays.
Safety Stock Inventory
Safety stock is an additional inventory held to buffer against unexpected demand fluctuations or supply disruptions. It provides a cushion to prevent stockouts and ensures uninterrupted production or customer fulfillment. However, holding excessive safety stock can lead to increased storage costs and obsolescence.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), Business inventories in economics
EOQ is a formula used to determine the optimal quantity of inventory to order at a time. It considers factors such as demand, holding costs, and ordering costs to minimize total inventory costs.
Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
VMI is a partnership between a buyer and a supplier, where the supplier manages the buyer’s inventory levels based on predetermined parameters. It reduces the buyer’s workload, improves inventory accuracy, and strengthens supplier relationships.
Technology in Inventory Management
Technology has revolutionized inventory management. Inventory management systems (IMS) automate inventory tracking, forecasting, and reordering. They provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and optimize stock levels.
Inventory Optimization and Supply Chain Management
Inventory optimization is crucial for supply chain efficiency as it ensures businesses have the right amount of inventory at the right time to meet customer demand while minimizing costs.
Forecasting and data analysis play a vital role in inventory optimization. Businesses analyze historical data, demand patterns, and market trends to predict future demand and optimize inventory levels accordingly.
Integration of Inventory Management into Supply Chain Strategies
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory:JIT aims to minimize inventory levels by receiving materials only when needed for production, reducing storage costs and improving cash flow.
- Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI):In VMI, suppliers manage the inventory levels of their customers, ensuring optimal stock levels and reducing the risk of stockouts.
- Safety Stock Management:Businesses maintain a buffer stock of safety inventory to mitigate the impact of unexpected demand fluctuations or supply chain disruptions.
Global Trends in Business Inventories

Global trends in business inventories have a significant impact on economic growth. Globalization, technology, and consumer behavior have transformed inventory management practices, leading to changes in inventory levels and their impact on the economy.
Globalization has increased the interconnectedness of businesses worldwide, leading to complex supply chains and the need for efficient inventory management. Technology has also played a vital role in improving inventory tracking and optimization, enabling businesses to reduce inventory levels while maintaining high levels of customer service.
Effects of Globalization on Inventory Management
- Increased complexity of supply chains, requiring sophisticated inventory management systems.
- Increased competition, driving businesses to optimize inventory levels to reduce costs.
- Greater access to global markets, allowing businesses to source goods from multiple locations, potentially reducing inventory levels.
Effects of Technology on Inventory Management
- Improved inventory tracking and optimization, reducing the need for high inventory levels.
- Real-time inventory data, enabling businesses to make informed decisions about inventory levels.
- Automated inventory management systems, reducing human error and improving efficiency.
Effects of Consumer Behavior on Inventory Management
- Increased demand for customization and personalization, leading to higher inventory levels for specialized products.
- Shorter product lifecycles, requiring businesses to manage inventory levels carefully to avoid obsolescence.
- Growth of e-commerce, requiring businesses to adapt inventory management strategies to meet the demands of online retail.
Role of International Trade in Inventory Levels
International trade plays a crucial role in inventory levels. Countries with high levels of imports may have lower inventory levels as they rely on foreign suppliers to meet demand. Conversely, countries with high levels of exports may have higher inventory levels to meet international demand.
Exchange rate fluctuations and trade policies can also impact inventory levels, as businesses may adjust their inventory strategies to mitigate risks and optimize profitability.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Businesses that effectively manage their inventories can gain a competitive advantage. Here are some case studies and examples to illustrate successful inventory management practices:
Walmart’s Inventory Management
Walmart, the world’s largest retailer, has a sophisticated inventory management system that uses technology to track inventory levels in real-time. This allows Walmart to optimize its inventory levels, reduce waste, and improve customer service.
- Walmart uses RFID tags to track inventory in its stores and warehouses.
- The company has developed a forecasting system that uses artificial intelligence to predict demand.
- Walmart’s inventory management system is integrated with its supply chain, allowing the company to quickly respond to changes in demand.
Amazon’s Inventory Optimization
Amazon, the e-commerce giant, uses inventory optimization to improve profitability. Amazon uses a variety of techniques to optimize its inventory, including:
- Using data analytics to identify slow-moving items and reduce inventory levels.
- Offering discounts on overstocked items to clear inventory.
- Using fulfillment centers located near customers to reduce shipping times and inventory holding costs.
Challenges and Best Practices in Inventory Management
Inventory management can be a complex and challenging task. Some of the challenges businesses face include:
- Managing inventory levels to meet demand while minimizing waste.
- Balancing the costs of holding inventory with the costs of stockouts.
- Dealing with seasonal fluctuations in demand.
Some of the best practices for inventory management include:
- Using technology to track inventory levels and forecast demand.
- Implementing inventory optimization techniques to reduce waste and improve profitability.
- Collaborating with suppliers to ensure a reliable supply of goods.
Closure: Business Inventories In Economics
In conclusion, business inventories in economics are a multifaceted and dynamic aspect that influences economic growth, stability, and supply chain efficiency. By optimizing inventory levels and implementing effective management strategies, businesses can enhance profitability, reduce costs, and contribute to overall economic well-being.
FAQ Summary
What is the significance of business inventories in economics?
Business inventories are crucial in economics as they represent the stock of goods held by businesses at any given time. They influence economic indicators such as GDP, employment, and inflation, and serve as an economic indicator, reflecting the health of the economy.
How do businesses manage inventory levels?
Businesses employ various inventory management techniques, including just-in-time (JIT), first-in-first-out (FIFO), and last-in-first-out (LIFO). The choice of technique depends on factors such as industry, product type, and business objectives.
What is the role of technology in inventory management?
Technology has revolutionized inventory management, enabling businesses to automate processes, track inventory in real-time, and optimize stock levels using forecasting and data analysis. This has led to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced supply chain visibility.
 wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY
wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY