Business inventories econ, a crucial aspect of economic activity, plays a significant role in economic growth, stability, and business operations. This article delves into the concept, importance, and management of business inventories, examining their impact on production, employment, and inflation, as well as the role of technology and global supply chains in inventory management.
Effective inventory management is essential for businesses to optimize costs, minimize waste, and meet customer demand. This article explores common inventory management strategies, challenges, and opportunities, providing valuable insights for businesses seeking to enhance their inventory practices.
Business Inventory Overview
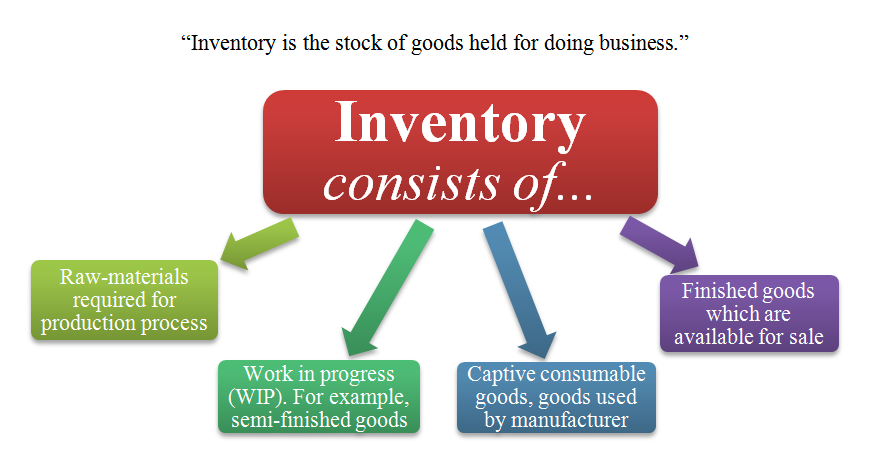
Business inventories refer to the stock of finished goods, work-in-progress, and raw materials held by businesses to meet customer demand and ensure smooth operations. Inventories play a crucial role in the economy, enabling businesses to respond to fluctuations in demand and maintain production schedules.
Types of Business Inventories
There are three main types of business inventories:
- Raw materials inventory:These are materials that have not yet been processed or used in production.
- Work-in-progress inventory:These are goods that are partially completed and still undergoing production.
- Finished goods inventory:These are goods that are ready for sale to customers.
Importance of Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is essential for businesses to optimize their operations and profitability. It involves:
- Maintaining optimal inventory levels to meet customer demand without overstocking or understocking.
- Minimizing inventory costs, such as storage, handling, and obsolescence.
- Improving production efficiency by ensuring a steady supply of raw materials and work-in-progress.
Economic Impact of Business Inventories

Business inventories have a significant impact on economic growth and stability. They affect production, employment, and inflation, influencing overall economic conditions.
High inventory levels can lead to excess production, resulting in a decline in prices and reduced profits. Conversely, low inventory levels can lead to shortages, causing price increases and potential economic instability.
Impact on Production and Employment
Inventory levels directly influence production decisions. When inventories are high, businesses may reduce production to avoid overstocking. This can lead to lower output, reduced employment, and slower economic growth.
Conversely, low inventory levels may prompt businesses to increase production to meet demand. This can lead to higher output, increased employment, and faster economic growth.
Impact on Inflation
Inventory levels can also impact inflation. When inventories are high, businesses may offer discounts to reduce excess stock. This can lead to lower prices and reduced inflation.
On the other hand, low inventory levels can lead to higher prices as businesses struggle to meet demand. This can contribute to increased inflation.
Role of Government Policies
Governments play a role in managing business inventories through monetary and fiscal policies.
- Monetary policy, such as interest rate adjustments, can influence borrowing costs for businesses, affecting their inventory investment decisions.
- Fiscal policy, such as tax incentives or subsidies, can encourage or discourage businesses from holding higher or lower inventory levels.
Inventory Management Strategies

Inventory management is crucial for businesses to balance costs, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. Different strategies are employed to optimize inventory levels, minimize waste, and maximize profits.
Common inventory management strategies include:
Just-in-Time (JIT)
JIT aims to minimize inventory by ordering and receiving items only when they are needed for production or sale. This strategy reduces holding costs but requires accurate forecasting and a reliable supply chain.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
EOQ calculates the optimal quantity of inventory to order at a time to minimize total inventory costs, including ordering, holding, and shortage costs.
Safety Stock
Safety stock is an additional inventory held as a buffer to protect against unexpected demand or supply chain disruptions. It increases inventory costs but reduces the risk of stockouts.
First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
FIFO assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first. This strategy helps prevent spoilage or obsolescence and ensures that customers receive fresh products.
Last-In, First-Out (LIFO)
LIFO assumes that the most recently purchased inventory is sold first. This strategy can result in higher inventory costs during periods of inflation but may provide tax advantages.
Challenges and Opportunities
Inventory management strategies present challenges and opportunities:
- Balancing costs and efficiency:Optimizing inventory levels to minimize costs while maintaining customer service levels.
- Forecasting accuracy:Accurate demand forecasting is essential for effective inventory management, especially for JIT and EOQ strategies.
- Supply chain disruptions:Unexpected events can disrupt supply chains, making it challenging to maintain optimal inventory levels.
- Technological advancements:Inventory management software and data analytics can enhance forecasting accuracy and improve inventory optimization.
- Customer service:Maintaining adequate inventory levels is crucial for meeting customer demand and avoiding stockouts.
Technological Advancements in Inventory Management: Business Inventories Econ
Technological advancements have revolutionized inventory management practices, enabling businesses to track, monitor, and manage their inventories with greater efficiency and accuracy.
One of the most significant impacts of technology on inventory management has been the introduction of automated inventory systems. These systems use sensors, RFID tags, and other technologies to track inventory levels in real-time, eliminating the need for manual counting and reducing the risk of errors.
Innovative Technologies, Business inventories econ
- RFID tags:Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags are small electronic devices that can be attached to individual items or pallets, allowing them to be tracked and identified using radio waves.
- Barcode scanners:Barcode scanners use lasers or cameras to read barcodes printed on items, providing quick and accurate identification for inventory tracking.
- Inventory management software:Inventory management software provides a centralized platform for managing inventory data, including item information, stock levels, and reorder points.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI algorithms can analyze inventory data to identify trends, predict demand, and optimize inventory levels.
These technologies have numerous benefits, including:
- Improved accuracy and reduced errors in inventory counting
- Real-time visibility into inventory levels
- Automated inventory replenishment and order processing
- Optimized inventory levels and reduced carrying costs
- Enhanced customer service through improved order fulfillment
However, there are also some limitations to consider:
- Cost:Implementing and maintaining automated inventory systems can be expensive.
- Complexity:These systems can be complex to implement and require specialized knowledge to operate.
- Data security:Automated inventory systems store sensitive inventory data, which can be vulnerable to cyber threats.
Overall, technological advancements have significantly improved inventory management practices, providing businesses with greater efficiency, accuracy, and control over their inventories.
Global Supply Chains and Business Inventories
In today’s globalized economy, businesses rely heavily on complex supply chains that span multiple countries and continents. This has significant implications for business inventory management, as companies must navigate the challenges and opportunities of sourcing and managing inventory from diverse locations.
Global Sourcing and Logistics
Global sourcing allows businesses to access a wider range of suppliers and materials at potentially lower costs. However, it also introduces additional complexities, such as:
- Increased lead times and transportation costs
- Currency fluctuations and exchange rate risks
- Customs regulations and import/export restrictions
Effective logistics management is crucial to mitigate these challenges. Companies must optimize transportation routes, manage inventory levels across multiple locations, and ensure timely delivery of goods.
Challenges and Opportunities
Managing inventories in a globalized economy presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses:
- Challenges:Managing inventory across multiple locations, dealing with transportation delays and disruptions, coping with currency fluctuations
- Opportunities:Access to a wider range of suppliers, potential cost savings through global sourcing, increased flexibility in responding to demand fluctuations
By carefully navigating these challenges and leveraging the opportunities, businesses can optimize their inventory management strategies in a globalized economy.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, business inventories econ is a complex and dynamic field that requires careful planning, management, and adaptation to changing market conditions. By understanding the economic impact of inventories and implementing effective inventory management strategies, businesses can improve their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance their overall competitiveness.
FAQ Explained
What is the role of business inventories in the economy?
Business inventories serve as a buffer between production and consumption, ensuring a smooth flow of goods and services to meet customer demand and minimize disruptions in supply chains.
How do inventory levels impact production and employment?
High inventory levels can lead to overproduction and reduced demand, resulting in layoffs and economic slowdown. Conversely, low inventory levels can cause shortages and production delays, affecting employment and economic growth.
What are some common inventory management strategies?
Common inventory management strategies include just-in-time (JIT), first-in, first-out (FIFO), last-in, first-out (LIFO), and periodic inventory review. Businesses choose the most appropriate strategy based on their specific needs and industry practices.
 wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY
wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY