Business accounting inventory plays a pivotal role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of financial statements. By effectively managing and valuing inventory, businesses can gain valuable insights into their operations, make informed decisions, and prevent costly errors.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of business accounting inventory, covering essential concepts, methods, and best practices. From inventory management to software solutions, we’ll explore everything you need to know to optimize your inventory processes and drive business success.
Inventory Management and Business Accounting
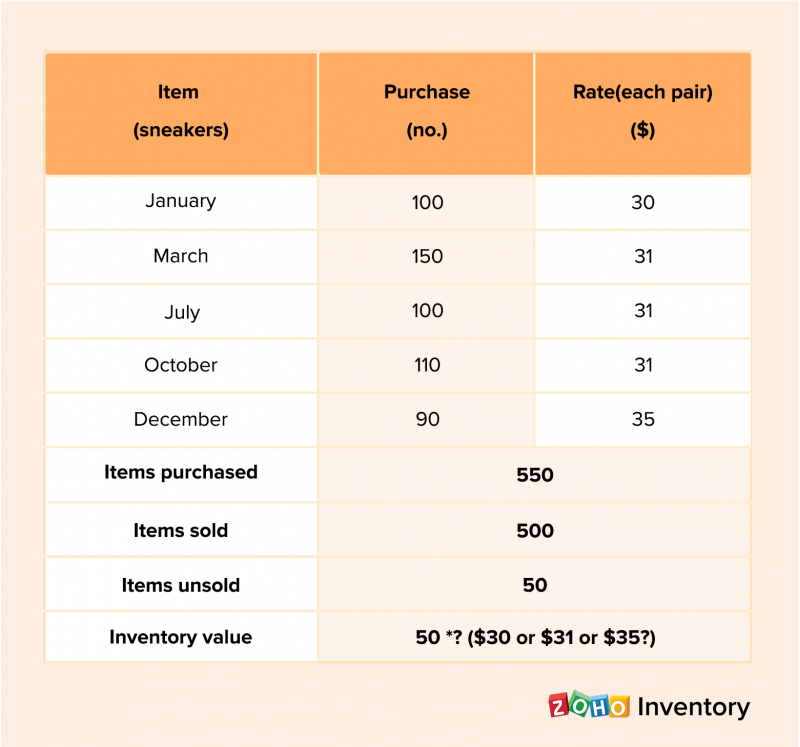
Inventory management plays a crucial role in business accounting by providing accurate and timely information about the quantity and value of inventory on hand. This information is essential for preparing financial statements, such as the balance sheet and income statement, which are used to assess the financial health of a company.
Inventory management also impacts financial ratios, such as inventory turnover and days sales in inventory, which are used to evaluate a company’s efficiency in managing its inventory.
Methods of Tracking and Valuing Inventory
There are several methods used to track and value inventory in accounting, including:
- First-in, first-out (FIFO): Assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first.
- Last-in, first-out (LIFO): Assumes that the most recently purchased inventory is sold first.
- Weighted average cost: Calculates the average cost of inventory on hand based on the cost of all purchases during a period.
Inventory Accounting Procedures: Business Accounting Inventory

Inventory accounting procedures involve the recording of transactions related to inventory in the accounting records. These procedures help businesses track the flow of inventory and ensure that the inventory is valued correctly.Inventory accounting procedures typically involve the following steps:
- Recording inventory purchases:When a business purchases inventory, the transaction is recorded in the accounting records by debiting the inventory asset account and crediting the accounts payable account.
- Recording inventory sales:When a business sells inventory, the transaction is recorded in the accounting records by debiting the cost of goods sold account and crediting the inventory asset account.
- Adjusting inventory levels:At the end of each accounting period, businesses must adjust their inventory levels to reflect any changes in the quantity of inventory on hand. This is done by taking a physical inventory count and comparing it to the inventory records.
Any differences between the physical inventory count and the inventory records are recorded in the accounting records as inventory adjustments.
Inventory Accounts
Inventory accounting procedures utilize various inventory accounts to track the flow of inventory. These accounts include:
- Inventory asset accounts:These accounts represent the value of the inventory on hand. There are two main types of inventory asset accounts: raw materials inventory and finished goods inventory.
- Cost of goods sold accounts:These accounts represent the cost of the inventory that has been sold. The cost of goods sold is calculated by multiplying the number of units sold by the cost per unit.
Journal Entries Related to Inventory Transactions
The following are examples of journal entries related to inventory transactions:
- Recording inventory purchases:
Debit Inventory $10,000 Credit Accounts Payable $10,000 - Recording inventory sales:
Debit Cost of Goods Sold $5,000 Credit Inventory $5,000 - Adjusting inventory levels:
Debit Inventory $1,000 Credit Inventory Adjustment $1,000
Inventory Analysis and Reporting
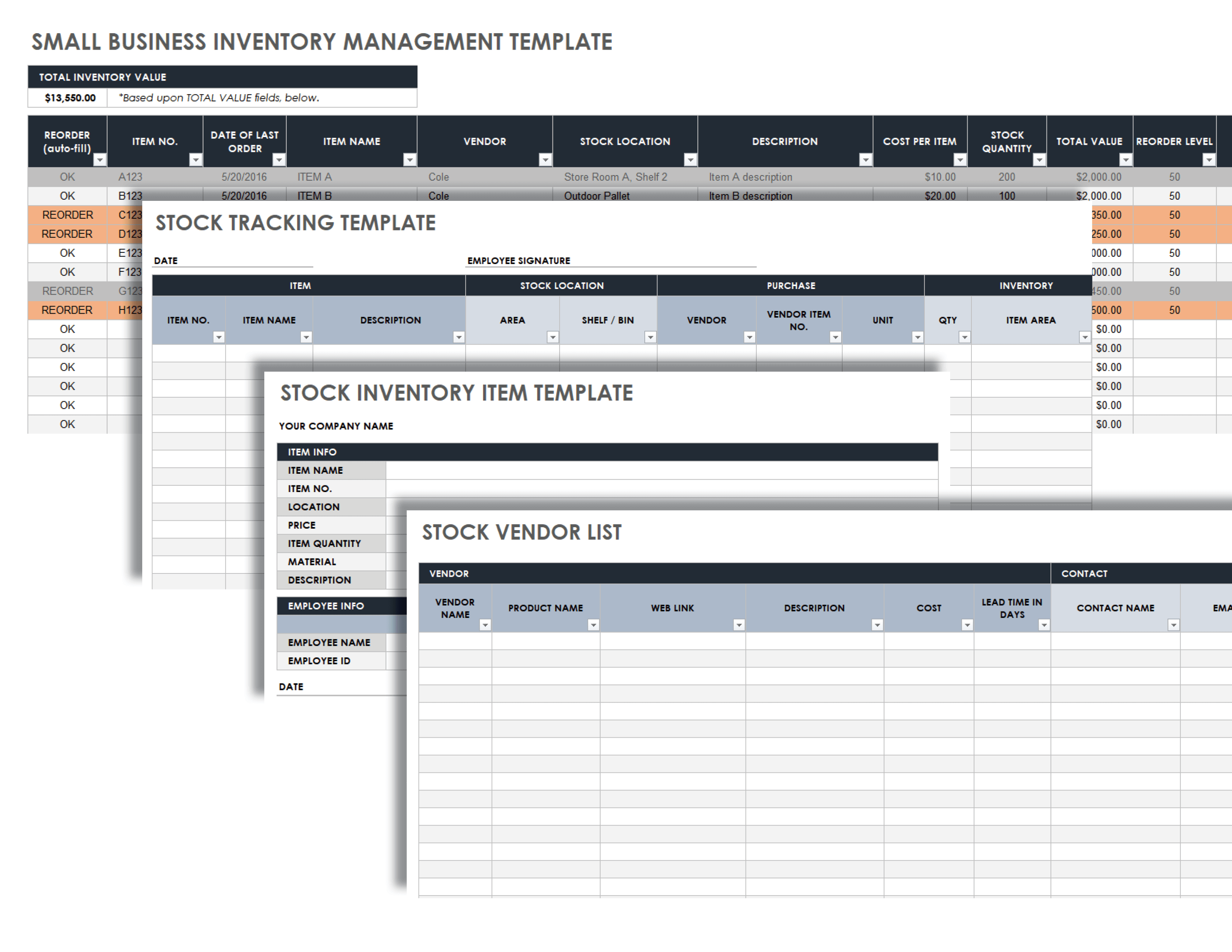
Inventory analysis and reporting are crucial aspects of business accounting that provide insights into inventory performance and support informed decision-making. By analyzing inventory data, businesses can optimize their inventory management practices, reduce costs, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Key Inventory Metrics
Several key metrics are used to analyze inventory performance:
Inventory Turnover
Measures the number of times inventory is sold and replaced within a specific period. A higher turnover indicates efficient inventory management and lower holding costs.
Days Sales in Inventory (DSI)
Represents the average number of days that inventory is held before being sold. A lower DSI indicates better inventory management and reduced carrying costs.
Importance of Inventory Analysis, Business accounting inventory
Inventory analysis is essential for:
Decision-Making
Provides valuable data for making informed decisions regarding inventory levels, purchasing strategies, and production planning.
Cost Optimization
Helps identify areas where inventory costs can be reduced, such as minimizing obsolete inventory or optimizing safety stock levels.
Performance Monitoring
Allows businesses to track inventory performance over time and identify trends or areas for improvement.
Inventory Report
An inventory report should include relevant data and insights, such as:
- Inventory Turnover and DSI metrics
- Inventory levels by category or product line
- Inventory aging analysis
- Recommendations for inventory management improvements
Regularly analyzing inventory data and generating reports enables businesses to gain a comprehensive understanding of their inventory performance, make data-driven decisions, and enhance their overall profitability.
Inventory Management Software
Inventory management software plays a vital role in business accounting, providing numerous benefits that enhance inventory accuracy and efficiency.
One of the primary advantages of using inventory management software is its ability to automate inventory tracking and record-keeping. This eliminates manual processes, reducing errors and saving time. The software provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing businesses to make informed decisions regarding stock levels, replenishment, and sales.
Software Comparison Table
Various inventory management software solutions are available, each with its unique features and capabilities. The following table compares some popular options:
| Software | Key Features | Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| NetSuite | Cloud-based ERP system with robust inventory management capabilities | Custom pricing based on business size and requirements |
| SAP Business One | Comprehensive ERP solution with inventory management, CRM, and financial management modules | Priced per user, starting at $50 per month |
| QuickBooks Commerce | Cloud-based inventory management software for small businesses | Starting at $25 per month |
| Fishbowl Inventory | On-premise inventory management software designed for manufacturers and distributors | Starting at $2,995 for a perpetual license |
| Brightpearl | Cloud-based inventory management and order management software for retailers | Custom pricing based on business size and requirements |
Improved Inventory Accuracy and Efficiency
Inventory management software significantly improves inventory accuracy by providing real-time updates and eliminating manual data entry errors. The software tracks inventory movements, such as purchases, sales, and adjustments, ensuring that inventory records are up-to-date and reliable.
Furthermore, inventory management software enhances efficiency by automating tasks such as inventory counting, reorder point calculation, and purchase order generation. This frees up valuable time for accounting staff, allowing them to focus on more strategic tasks.
Inventory Control and Internal Control
Inventory control is crucial for preventing theft and fraud by ensuring the accuracy and safeguarding of inventory assets. Internal controls play a vital role in protecting inventory by establishing policies and procedures that minimize the risk of loss or misuse.
Importance of Inventory Control
- Accurate inventory records provide a clear understanding of available stock, preventing overstocking or shortages.
- Effective inventory management reduces the risk of obsolete or damaged items, minimizing losses and optimizing storage space.
- Proper inventory control helps prevent unauthorized access and theft, safeguarding assets and reducing financial losses.
Role of Internal Controls
- Establishing clear policies and procedures for inventory handling, storage, and tracking.
- Implementing physical safeguards such as secure storage facilities, access control, and regular inventory counts.
- Segregating duties to minimize the risk of fraud or errors.
- Conducting regular audits and reviews to ensure compliance with internal controls and identify potential weaknesses.
Best Practices for Inventory Control and Internal Control
- Use automated inventory management systems to enhance accuracy and reduce manual errors.
- Implement regular inventory cycle counts to verify physical inventory against records.
- Establish clear authorization levels for inventory transactions to prevent unauthorized access.
- Train staff on inventory handling procedures and internal control policies.
- Regularly review and update inventory control and internal control measures to address evolving risks.
End of Discussion

In conclusion, business accounting inventory is a critical aspect of financial management that requires careful attention and effective strategies. By understanding the concepts and methods Artikeld in this guide, businesses can establish a robust inventory system that supports their growth, profitability, and long-term success.
Questions Often Asked
What is the significance of inventory management in business accounting?
Inventory management is crucial in business accounting as it provides accurate data for financial statements, helps businesses track their assets, and enables them to optimize their operations for profitability.
What are the different inventory valuation methods?
Common inventory valuation methods include FIFO (First-In, First-Out), LIFO (Last-In, First-Out), and weighted average cost. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on factors such as industry practices and business objectives.
How does inventory analysis help businesses make informed decisions?
Inventory analysis provides valuable insights into inventory performance, such as inventory turnover and days sales in inventory. By analyzing these metrics, businesses can identify areas for improvement, optimize their inventory levels, and make informed decisions about production, purchasing, and sales.
 wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY
wohnroom.biz.id BUSINESS INVENTORY